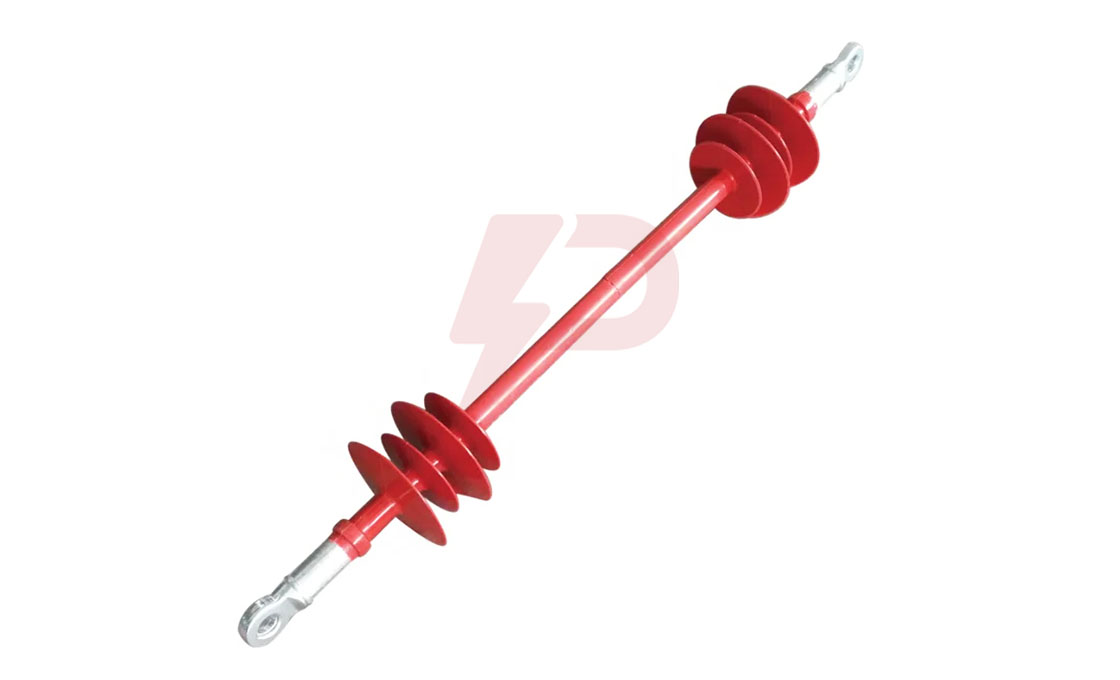
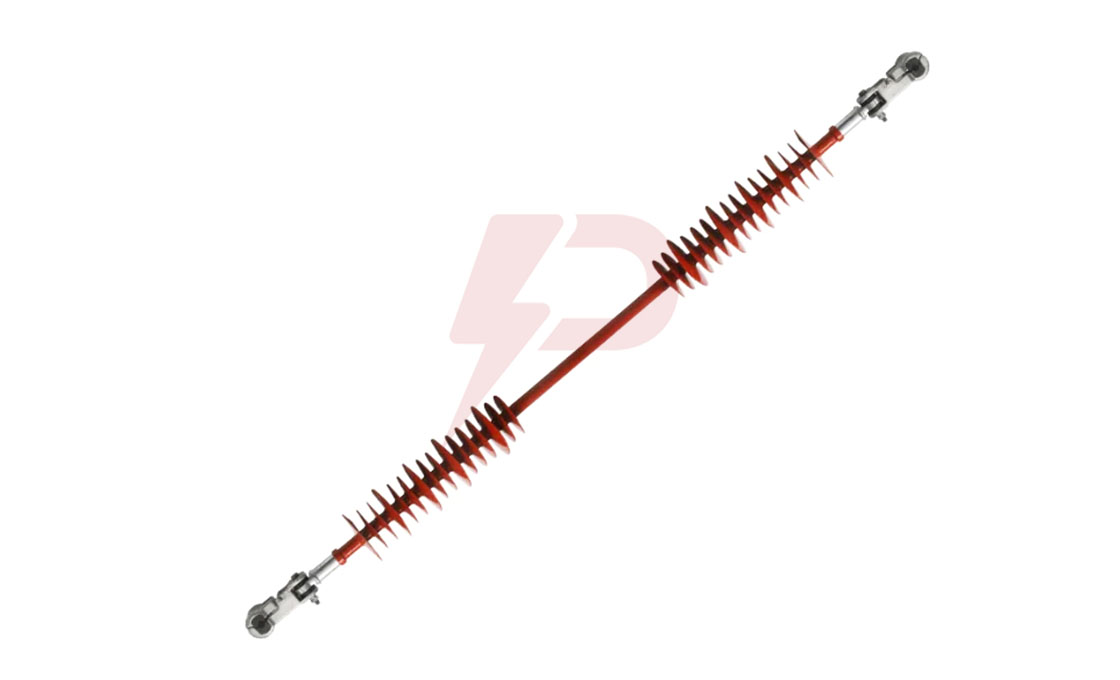
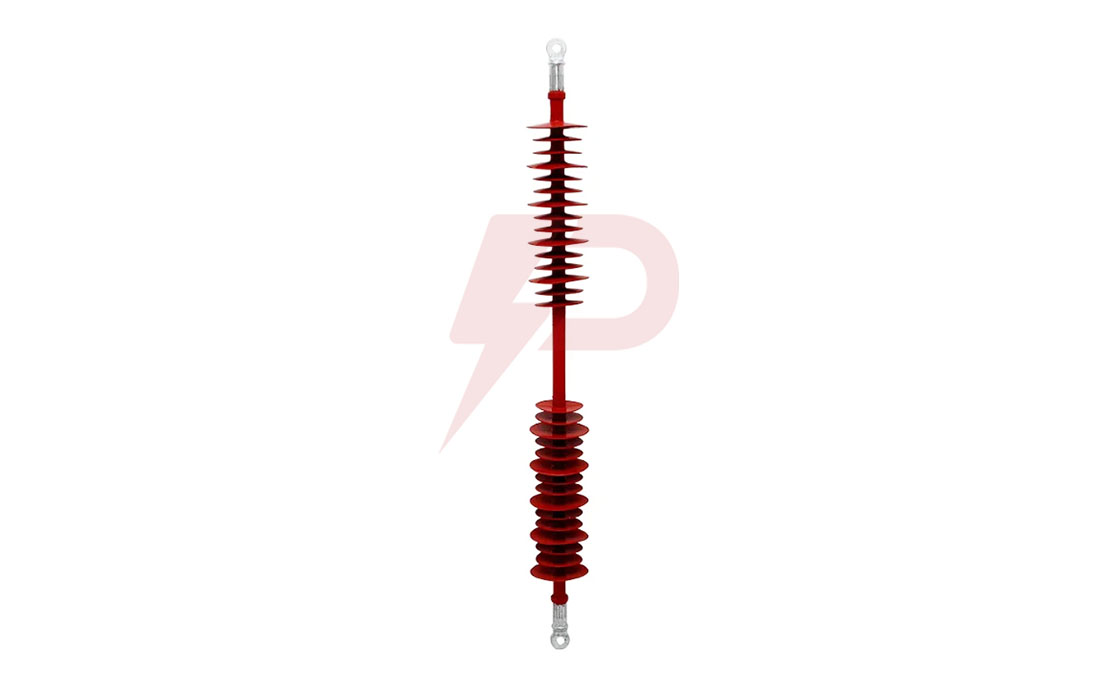
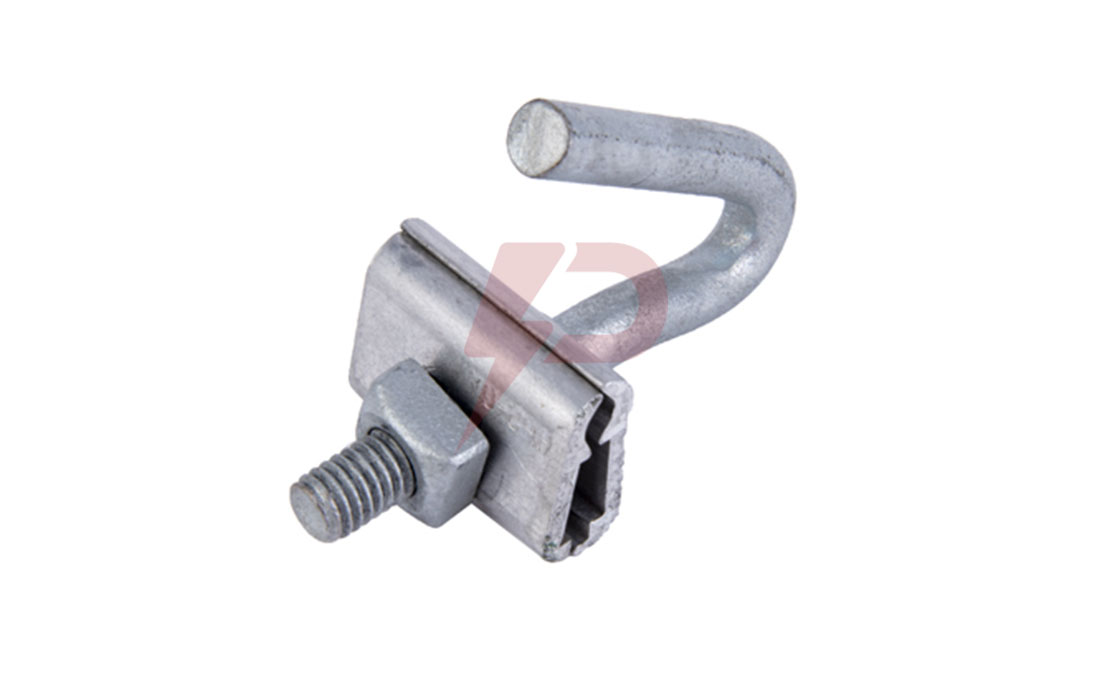
Interphase Spacer
The interphase spacer is an insulator mainly used to prevent mid-span flashovers caused by galloping and conductor jumping. Interphase spacers from Rax Industry are available in three varieties. They include segmental flexible, integrated flexible, and stiff interphase spacers. Integrated flexible and segmental flexible are the most common types of interphase spacers in the industry.
Interphase spacers function as a countermeasure for dealing with conductor galloping. They effectively reduce dynamic loads and galloping amplitude on transmission lines.
They work as anti-galloping insulators that mechanically connect the conductor of every phase. Their integration on the lines changes the characteristics of the system. They help restrain the movement of the conductor, controlling galloping in the process.
Interphase spacers are typically installed in the middle span. The first span mode is avoided because it is mainly excited when the ice shed on the entire span. Several methods of installation are used, including shorter span and longer span.
Important Features
- Composite material for absorbing vibrations
- Suit any voltage, configuration, and conductors
- Suitable for specific project requirements
- Field-adjustable spacer length for convenience purposes
- Material properties, electrical characteristics, and clamping system are modifiable
- Tested for ice-shedding oscillations and galloping
- Improves the reliability of the network
- Reduces network’s susceptibility to climate and weather events
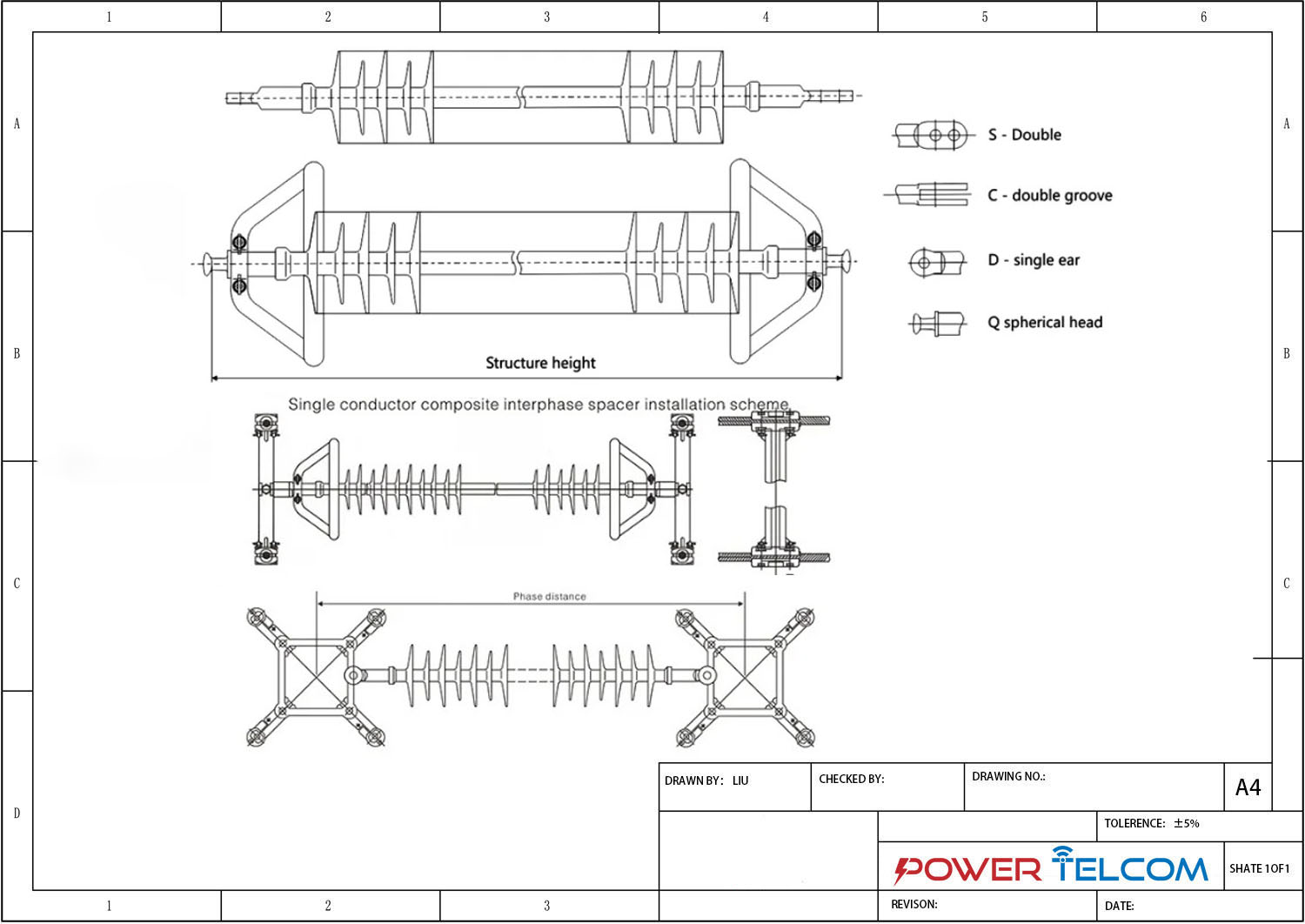
Interphase Spacer Drawing
| Model | Rated voltage KV | Phase distance MM | Rated tensile load KN | Rated bending load KN | Compression load resistant | Reverse tolerance to load N.m | Insulation distance MM | Minimum nominal creepage distance | Full wave impulse withstand voltage of lightning strike | Wet power frequency withstand voltage of |
| IS -66/70 | 66 | 2550 | 70 | 0.4 | 7 | 75 | 2260 | 300 | 410 | 185 |
| IS -110/70 | 110 | 2890 | 70 | 0.4 | 7.5 | 75 | 2600 | 4105 | 550 | 300 |
| IS -220/100 | 220 | 3150 | 100 | 0.4 | 7.5 | 75 | 2820 | 8500 | 1000 | 395 |
| IS -330/160 | 330 | 4650 | 160 | 0.4 | 10.5 | 75 | 4280 | 1180 | 1425 | 570 |
| IS -500/210 | 500 | 5900 | 210 | 0.4 | 12.5 | 75 | 5080 | 14400 | 2250 | 740 |
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
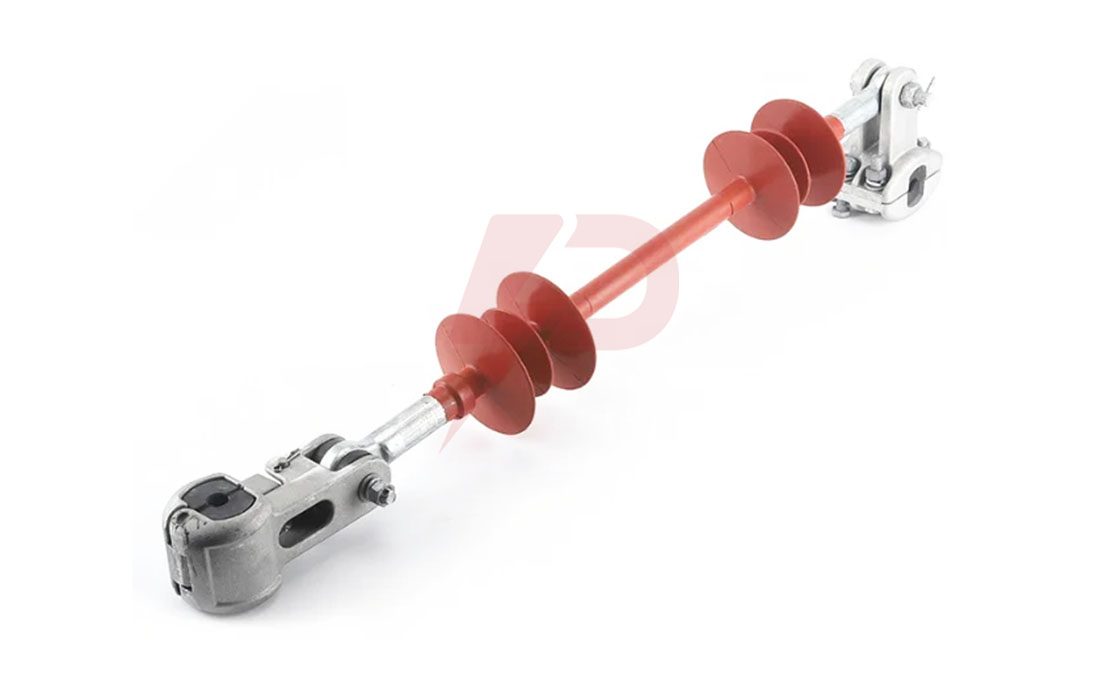

What Is an Interphase Spacer?
These are segmental flexible, stiff, or integrated flexible insulators that maintain conductor separation on transmission lines. They are used in transmission line applications to reduce the potential effect of ice build-up on the lines.
Primary Features of Interphase Spacers
Modern interphase spacers have a composite design that is lightweight and easy to install. Composite insulators have unique mechanical properties that improve their effectiveness. Every component of an interphase spacer is modifiable for improved versatility. Furthermore, the length of these anti-galloping devices can be adjusted in the field to meet specific project requirements.
Types of Interphase Spacers
Stiff Type
These are the traditional designs. They were engineered to be stiff because of their weight and the difficulty of installation and maintenance.
Integrated Flexible Type
Commonly used on transmission lines, these insulators are more flexible and stable than the stiff variety.
Segmental Flexible Type
Unlike the other two varieties, segmental flexible insulators have segmental structures. However, they are not the most effective ones for compression loading.
How an Interphase Spacer Works?
They have an insulating design that ensures phase-to-phase contact is avoided in the event of galloping. The interphase spacers force the galloping to move in a way that minimizes flashovers. Their effectiveness depends on their distribution along the span.