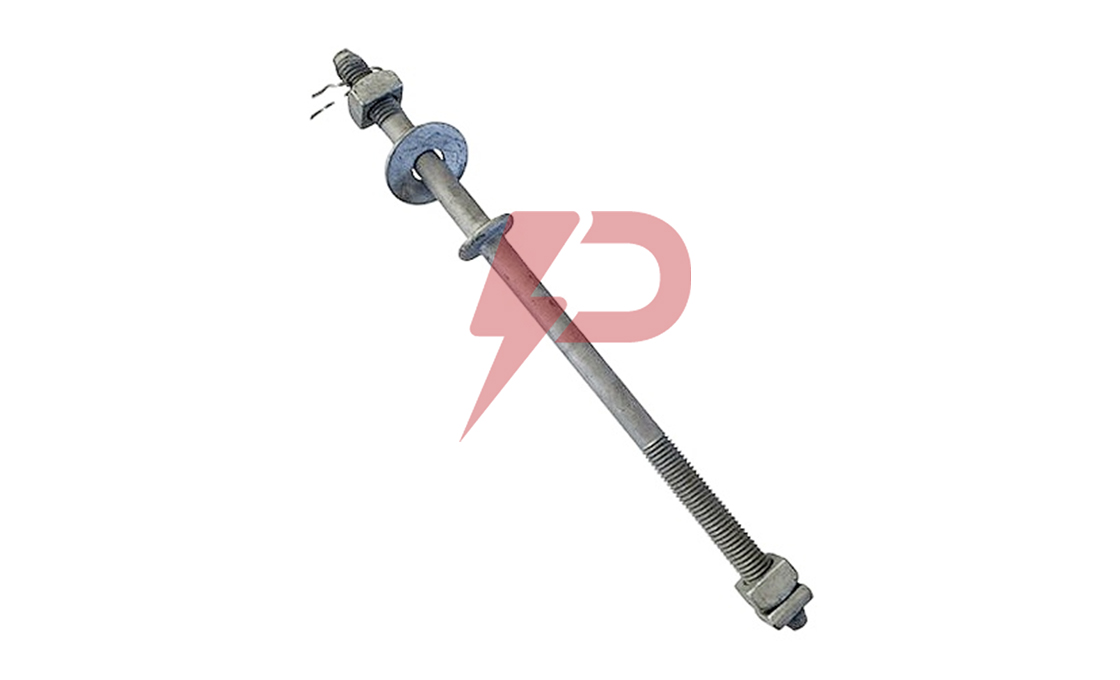
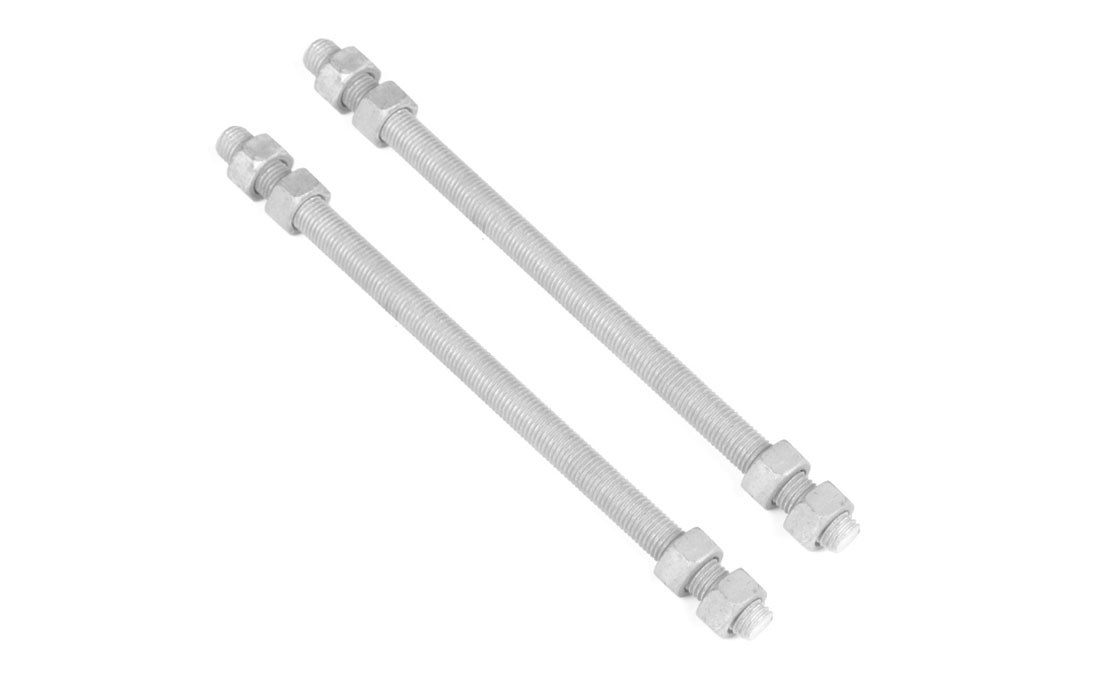
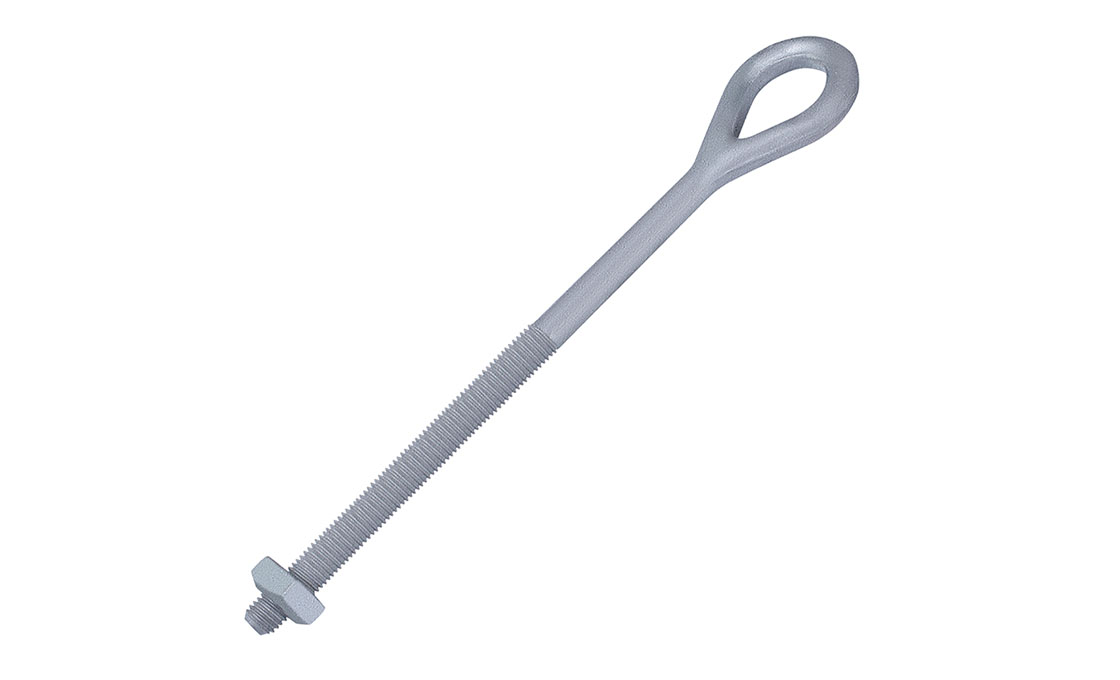
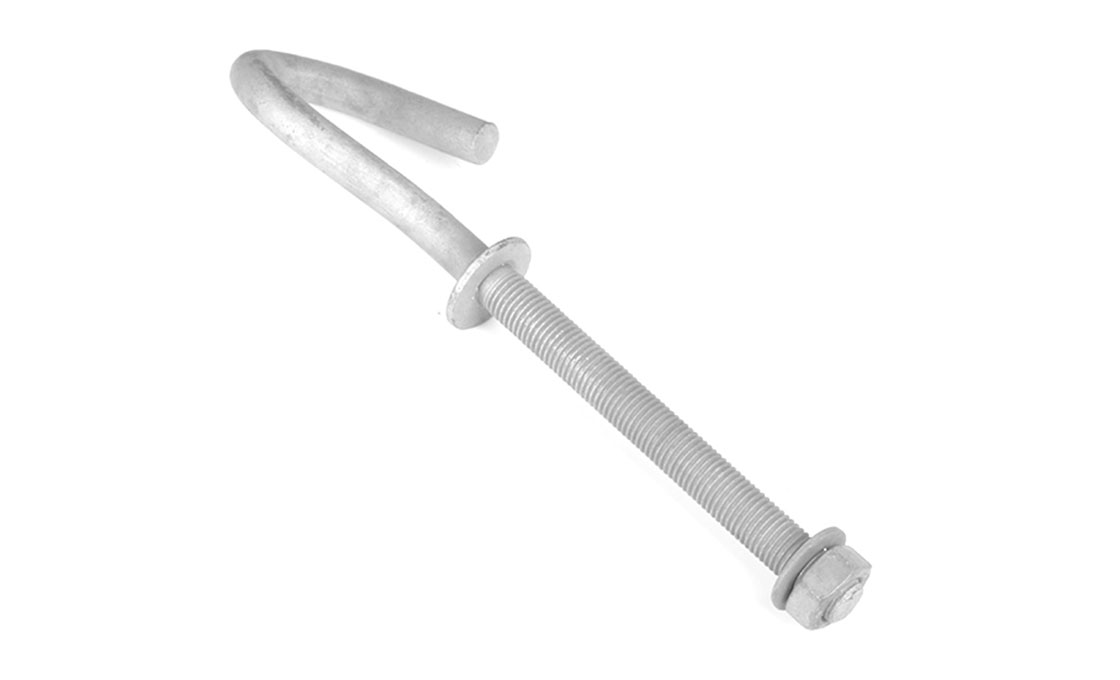
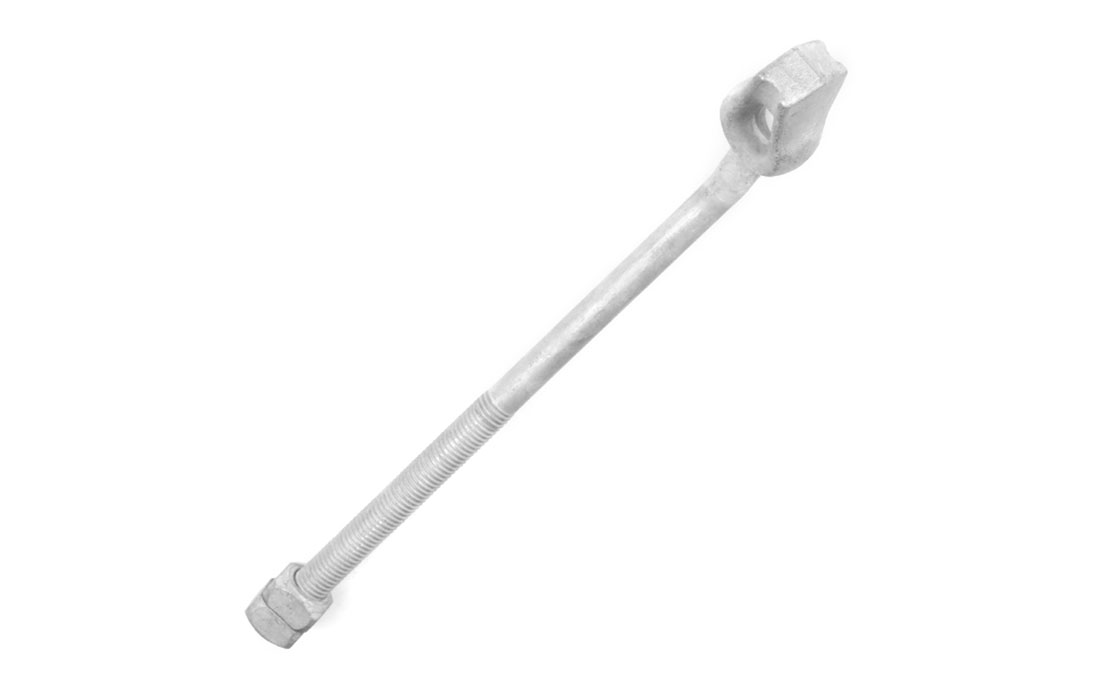
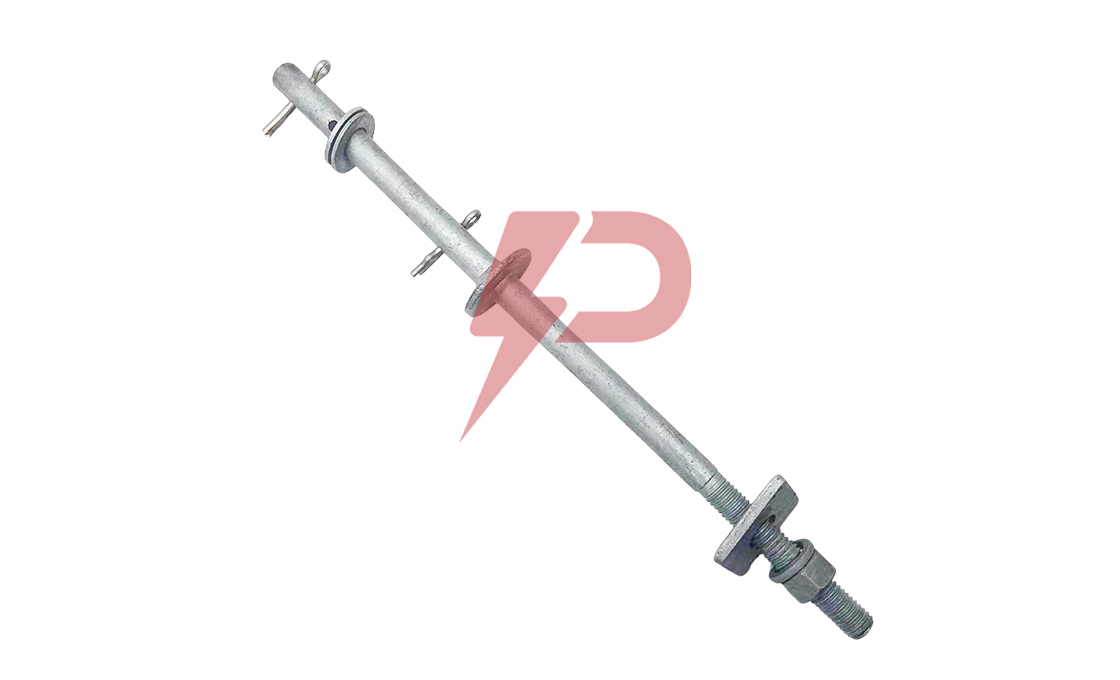
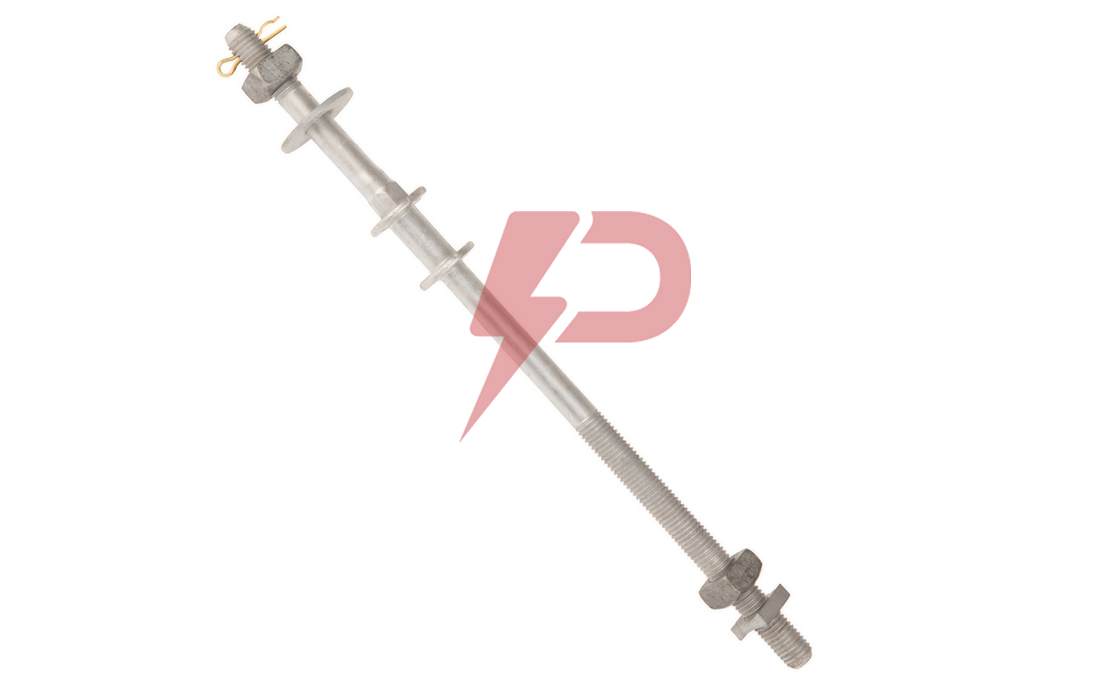
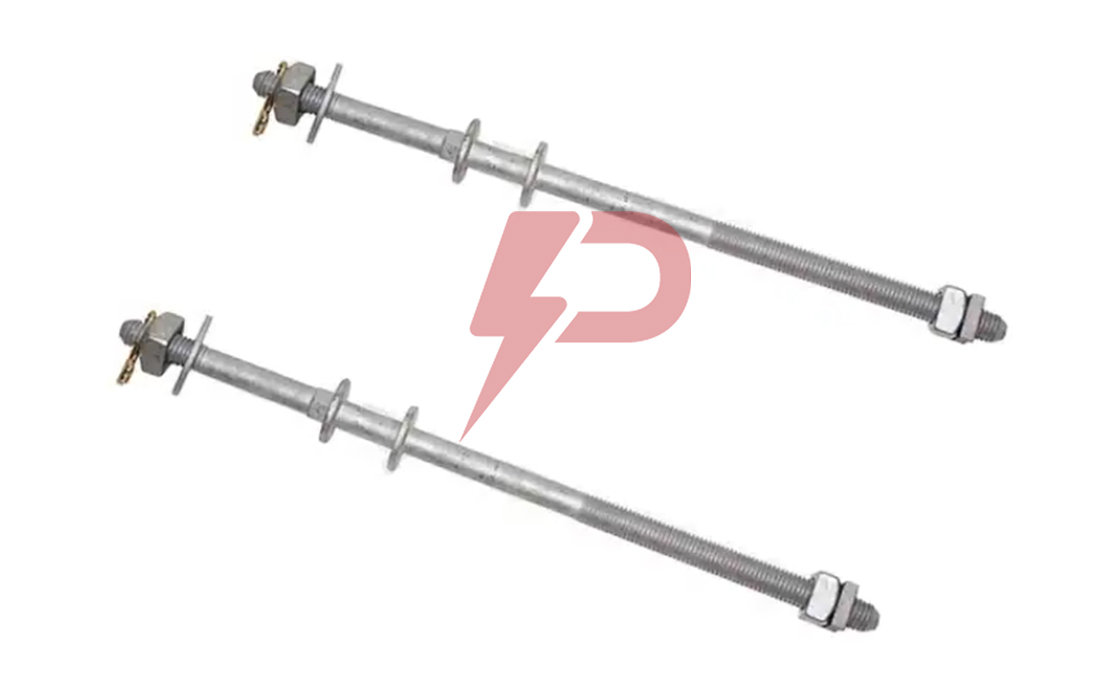
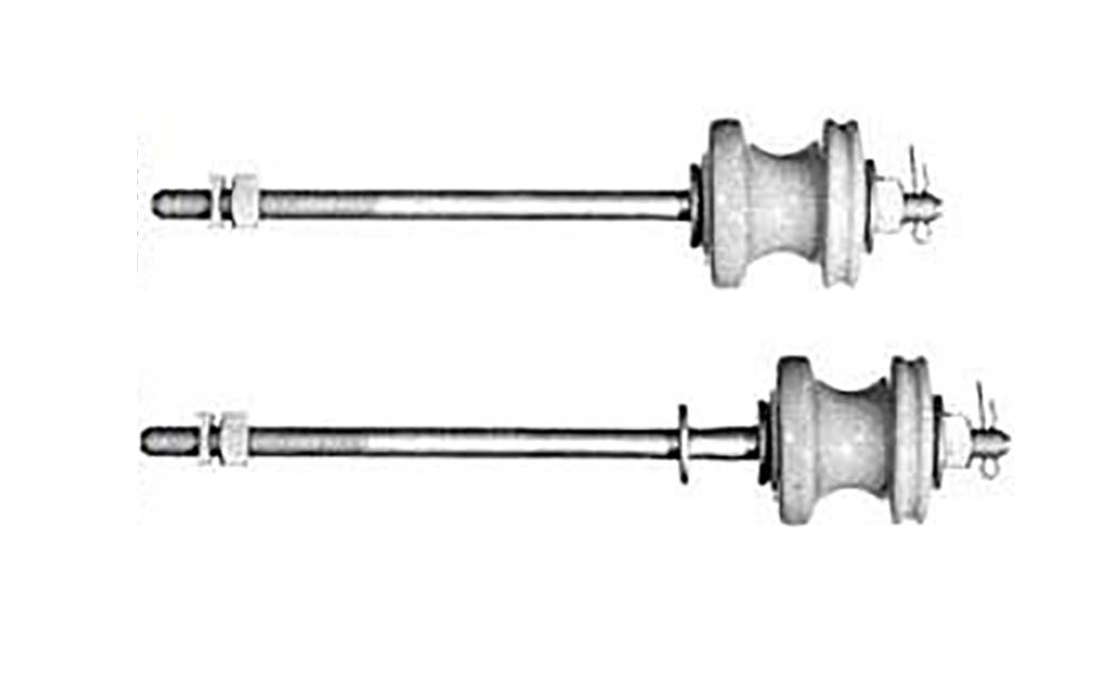
Upset Spool Bolt
Upset Bolts, also known as upset spool bolts or bolt upsets, are specialized fasteners designed for spool insulators in power line construction. These bolts consist of a steel shaft with forged plates at the insulator end, a threaded section (typically 5/8″ diameter), and a hole at the end with a steel pin to secure the insulator pin. Upset Bolts come in two types: single upset with forged plates on one side, and double upset with forged plates on both sides.
Upset Bolts are installed on the side of poles to support neutral conductors and power wires. Installation involves drilling holes in the pole, inserting the Upset Bolt through a spool insulator, and securing it with washers and nuts. The forged plate prevents the insulator pin from moving down, while the steel pin in the hole stops the insulator pin from coming out. They work in conjunction with spool insulators, guy wires, and other pole line hardware components.
Key Features:
• Hot-dip galvanized coating compliant with ASTM A-153 standards
• Forged plates for superior strength compared to welded construction
• 5/8-inch thread diameter with 6-inch thread length
• Available in various shank lengths from 12 to 14 inches
• Integral retainer system to secure insulator pins
• Minimum tensile strength of 13,550 pounds
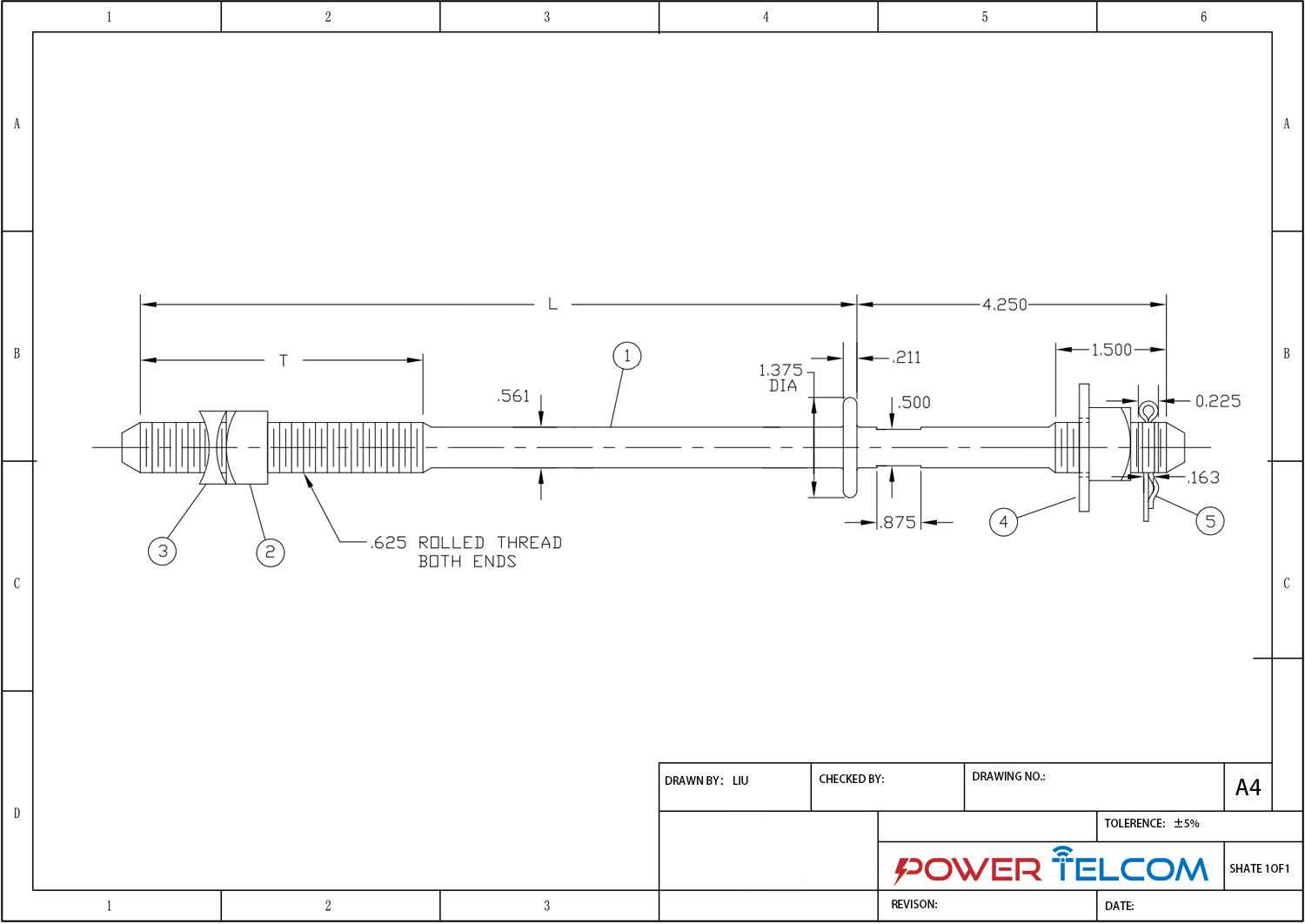
Upset Spool Bolt Drawing
| Stock No. | Rod Diameter Inch | Approximate Shipping WBight kg./100 Pcs. | Standard Pkg. Qty./ Carton | ||
| L | A | B | |||
| SUB0110-08 | 8 | 12-1/2 | 4 | 63.00 | 35 |
| SUB0110-09 | 9 | 13-1/3 | 4 | 68.00 | 30 |
| SUB0110-10 | 10 | 14-1/2 | 4 | 60.00 | 30 |
| SUB0110-12 | 12 | 16-1/2 | 6 | 80.00 | 30 |
| SUB0110-14 | 14 | 18-1/2 | 6 | 90.00 | 35 |
| DUB0111-08 | 8 | 14 | 4 | 73.00 | 30 |
| DUB0111-09 | 9 | 15 | 4 | 77.00 | 30 |
| DUB0111-10 | 10 | 16 | 4 | 65.00 | 35 |
| DUB0111-12 | 12 | 18 | 6 | 72.00 | 35 |
| DUB0111-14 | 14 | 20 | 6 | 80.00 | 35 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is an Upset Bolt?
An Upset Bolt is a specialized fastener designed for spool insulators, assembled on one side of a pole to support neutral conductors or power wires. It features forged plates at the insulator end to prevent the insulator pin from moving down, effectively fixing it in place to insulate conductors and secondary service wires.
What are the types of Upset Bolts?
There are two main types of Upset Bolts: single upset and double upset. The difference lies in the number of forged plates at the insulator end. Single upset bolts have fewer forged plates on one side, while double upset bolts have more forged plates on both sides of the bolt.
What are the key features of an Upset Bolt?
Upset Bolts typically have a 5/8″ thread diameter, a hole at the end with a steel pin to secure the insulator pin, and are hot-dip galvanized to ASTM A-153 standards. They often come with a round washer, square nuts, and a cotter pin for secure installation.
How are Upset Bolts installed?
Installation involves drilling holes on the side of the pole, positioning the bolt through the holes, and securing it with washers and nuts. The process requires careful alignment and proper tightening to ensure both mechanical stability and electrical conductivity when used in grounding systems.
What are the main applications of Upset Bolts?
Upset Bolts are primarily used in utility pole installations, supporting secondary service wires and neutral conductors. They’re essential in power distribution systems, communication infrastructure, and antenna installations where secure anchoring and electrical insulation are required.
What materials are Upset Bolts made from?
Upset Bolts are typically manufactured from high-strength structural steel. They often feature a special asphalt paint coating or hot-dip galvanization for corrosion protection, making them suitable for long-term outdoor use in various environmental conditions.
What sizes are available for Upset Bolts?
Upset Bolts come in various sizes, with common thread diameters of 5/8″. Lengths can range from 6 inches to over 14 inches, depending on the specific application. The size is often specified as diameter by length, such as “5/8″ x 14″”.
How do you select the right Upset Bolt?
Selection depends on factors like the required offset from the pole, load requirements, and environmental conditions. Consider the bolt’s tensile strength, thread length, and overall dimensions. For example, double upset bolts provide a 1-5/8″ offset from the pole.