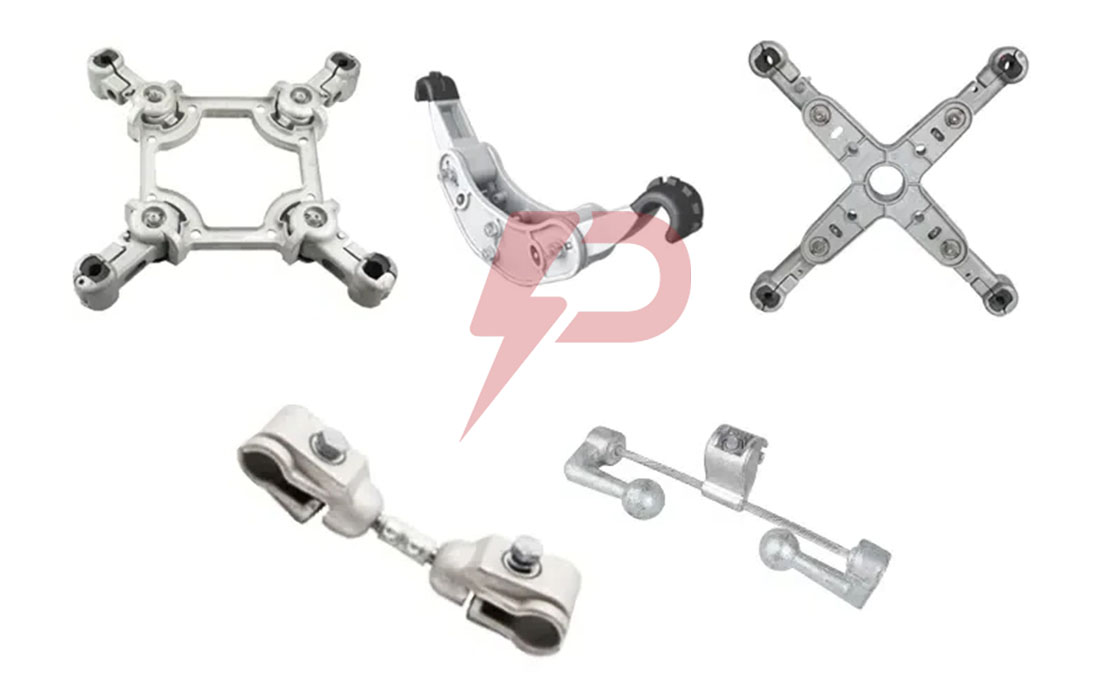
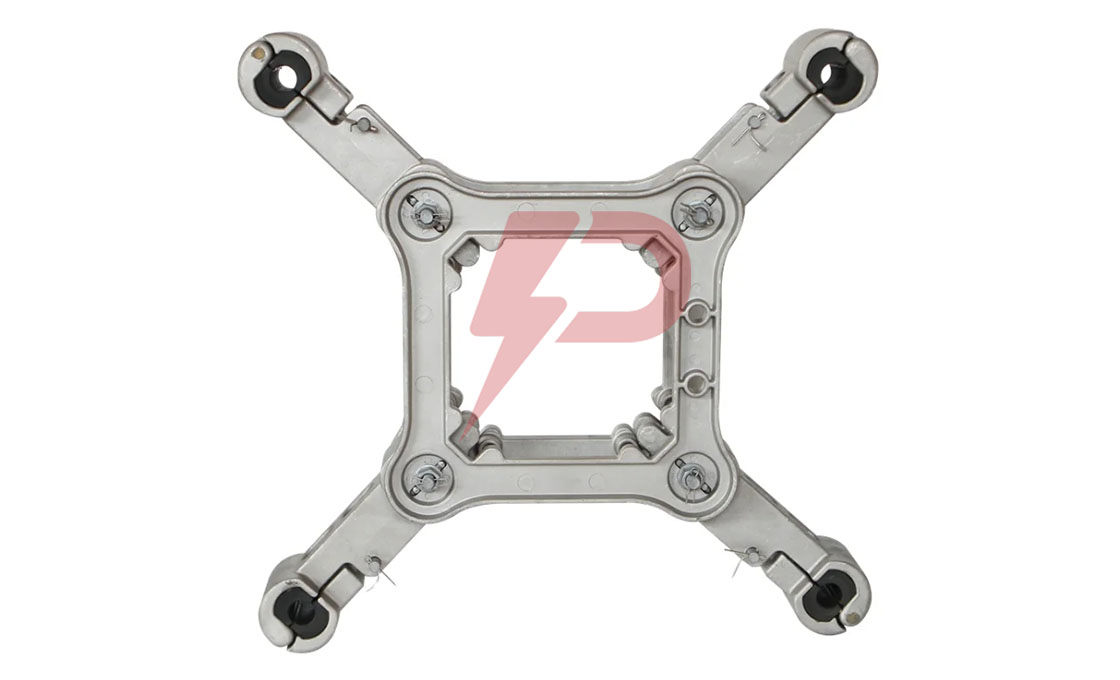
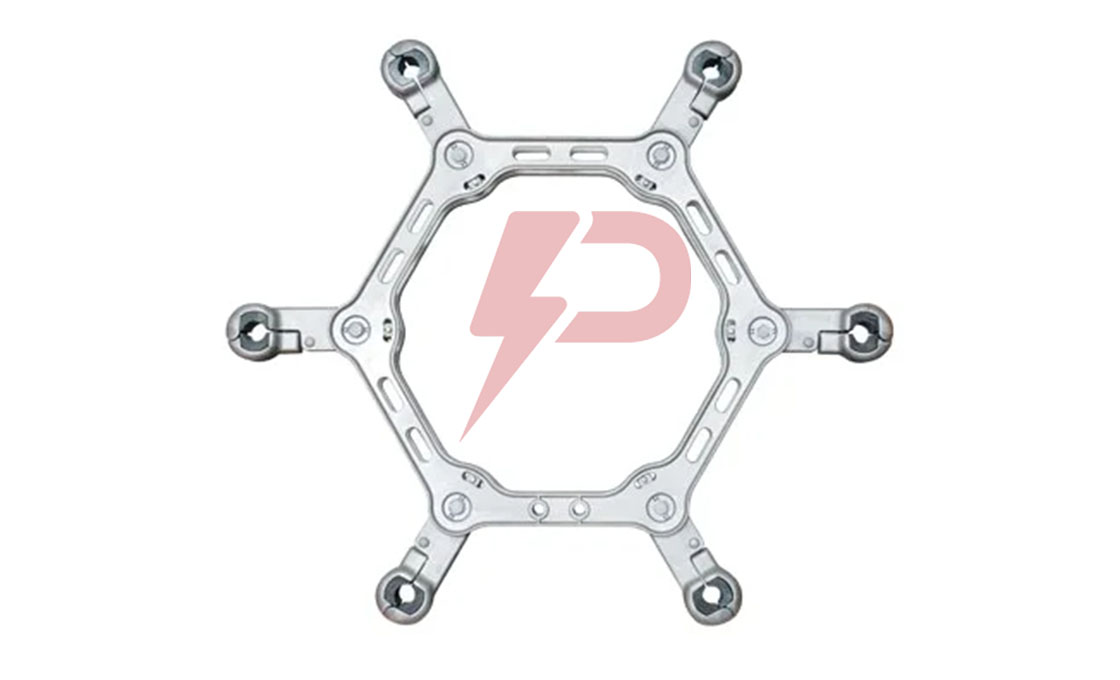
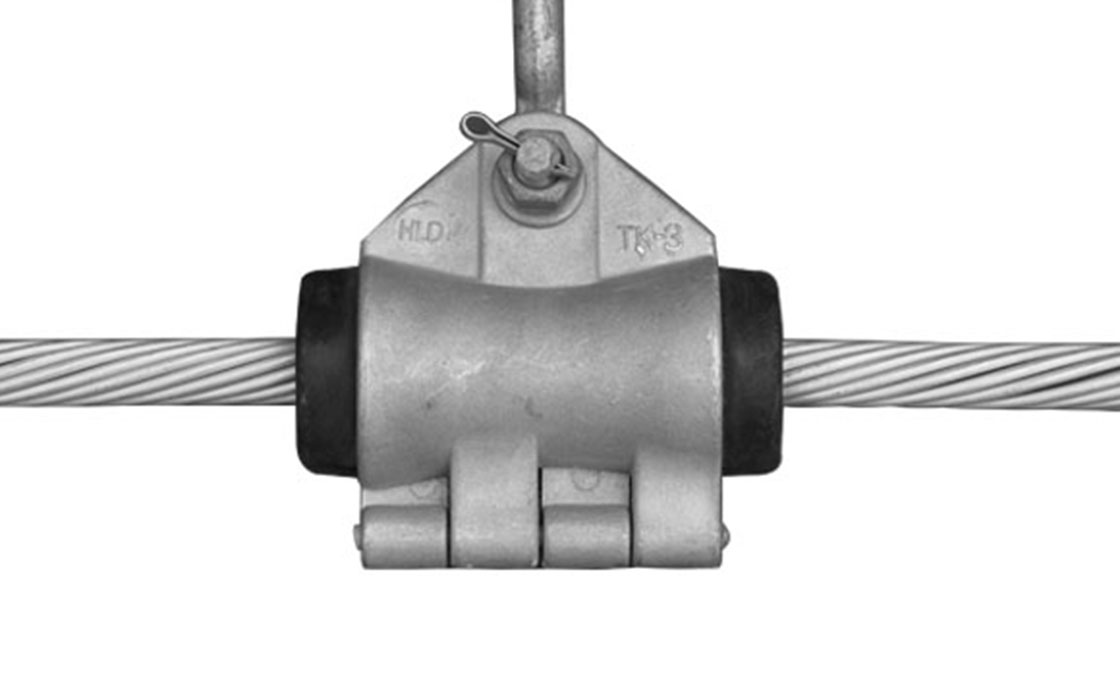
Spacer Damper
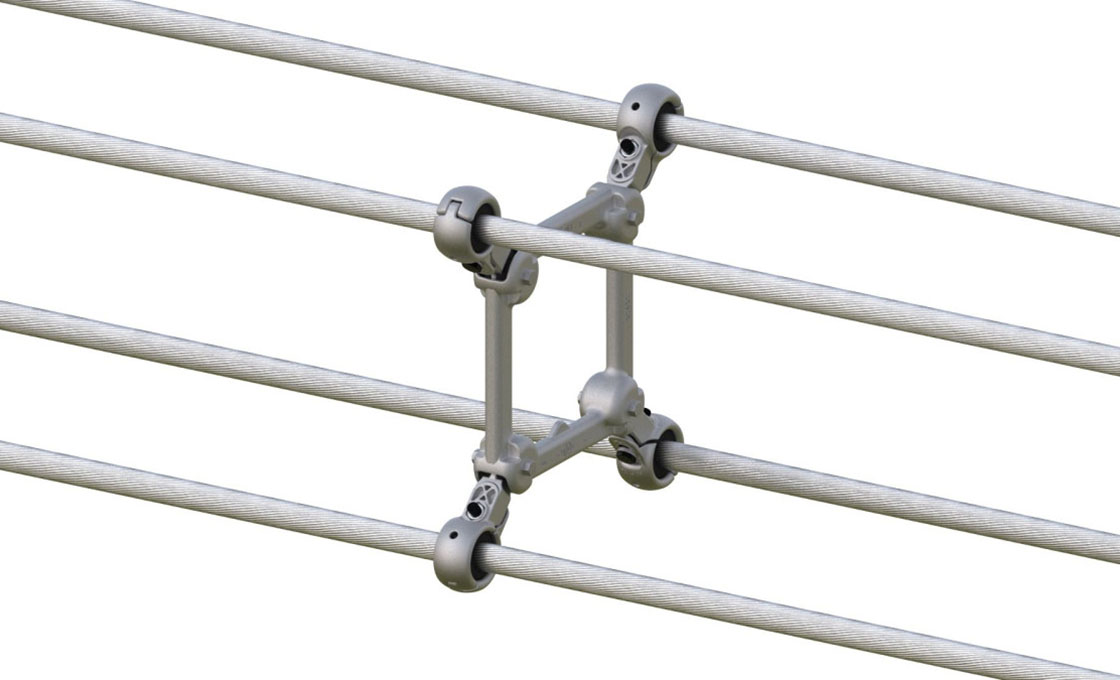
Spacer dampers are crucial devices installed in high-voltage transmission lines with bundled conductors to maintain uniform spacing and prevent conductor damage. These devices consist of a rigid frame with multiple arms connected through rubber bushings or elastomer elements, allowing for energy dissipation. The unique design of spacer dampers enables them to both maintain physical spacing and suppress wind-induced oscillations, including aeolian vibrations and galloping, which could otherwise lead to severe conductor damage and power outages.
The structure of spacer dampers incorporates elastomer parts between the frame and conductor clamps, positioned at intervals of 150 to 200 feet along transmission line spans. Spacer dampers come in various configurations to accommodate different bundle arrangements: twin (straight design for two conductors), triple (fan-shaped or triangular for three conductors), quadruple (square-shaped for four conductors), and hexagon designs. Each type maintains the same core function while adapting to specific conductor bundle requirements.
Features of spacer dampers:
• Maintains prescribed distance between sub-conductors
• Suppresses sub-span oscillations in bundle conductors
• Incorporates elastomer elements for energy dissipation
• Compatible with various bundle configurations
• Prevents conductor clashing and tilting
• Enhances transmission line reliability and longevity
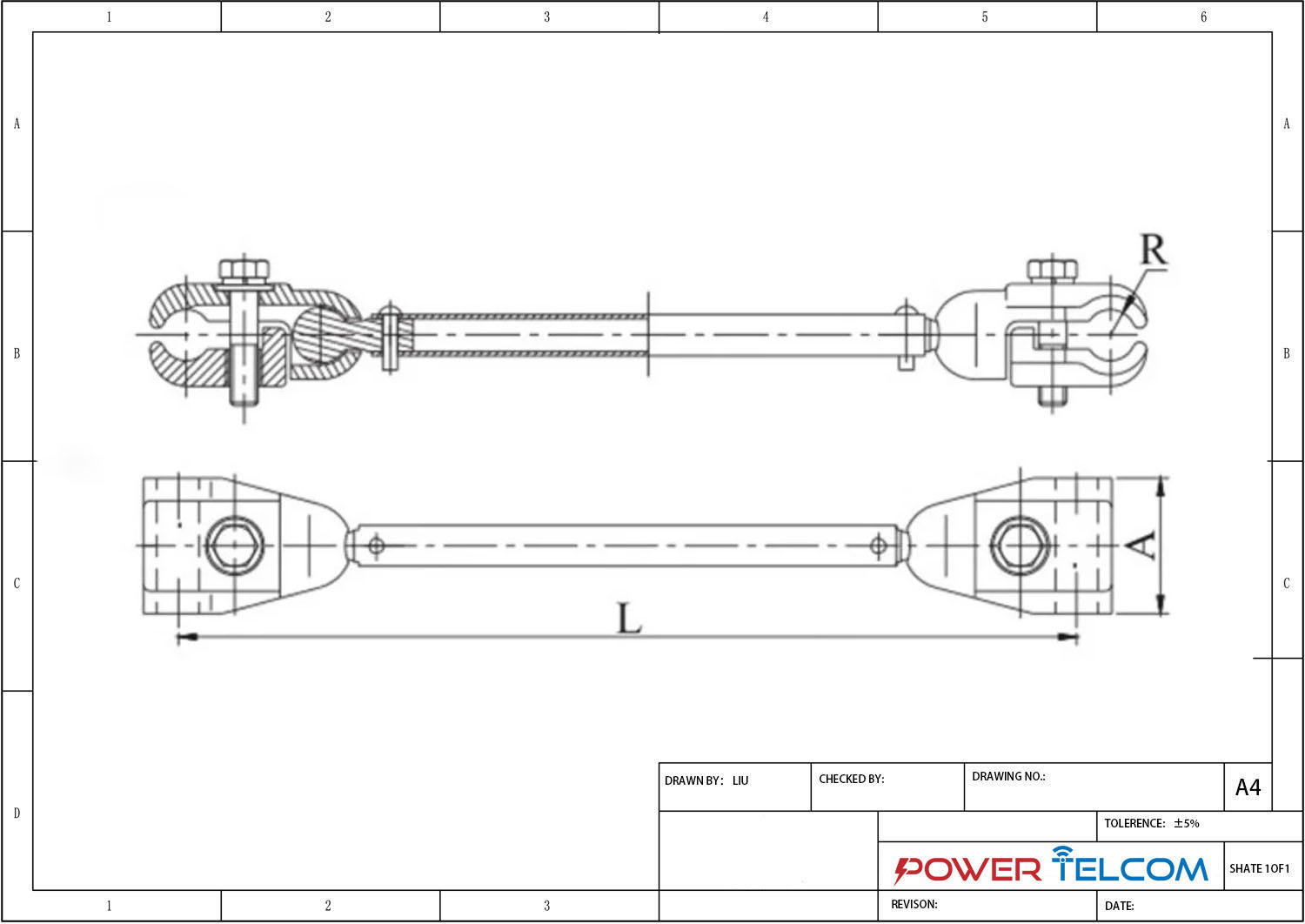
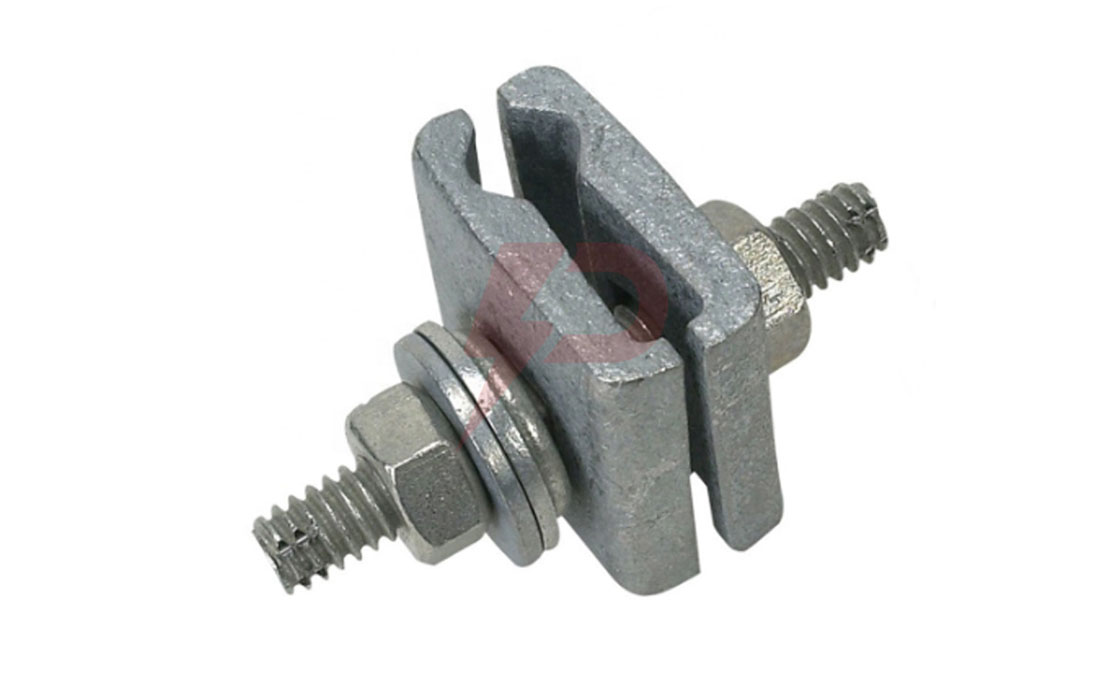
Twin Spacer damper Drawing
| Type | Applicable Conductor Section Area (mm2) | Dimension (mm) | Axial Load (kn) | ||
| A | R | L | |||
| FJQ (Z)-204 | 185-240 | 60 | 11 | 200 | 7 |
| FJQ (Z)-205 | 300-400 | 60 | 14.5 | 200 | 10 |
| FJQ (Z)-206 | 500-630 | 60 | 18 | 200 | 10 |
| FJQ (Z)-404 | 185-240 | 60 | 11 | 400 | 7 |
| FJQ (Z)-405 | 300-400 | 60 | 14.5 | 400 | 10 |
| FJQ (Z)-406 | 500-630 | 60 | 18 | 400 | 10 |
| FJQ (Z)-455 | 300-400 | 60 | 15.4 | 450 | 10 |
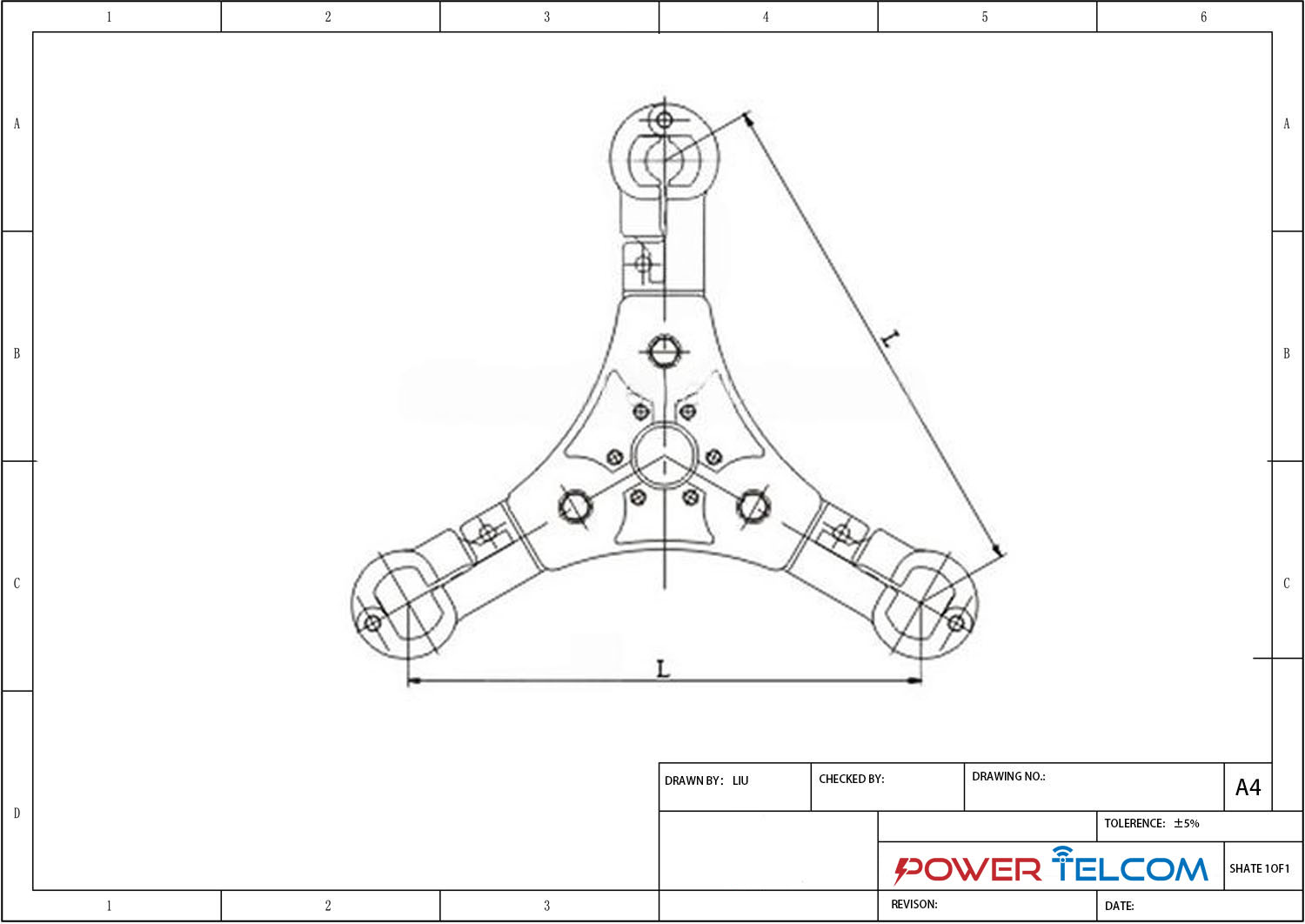
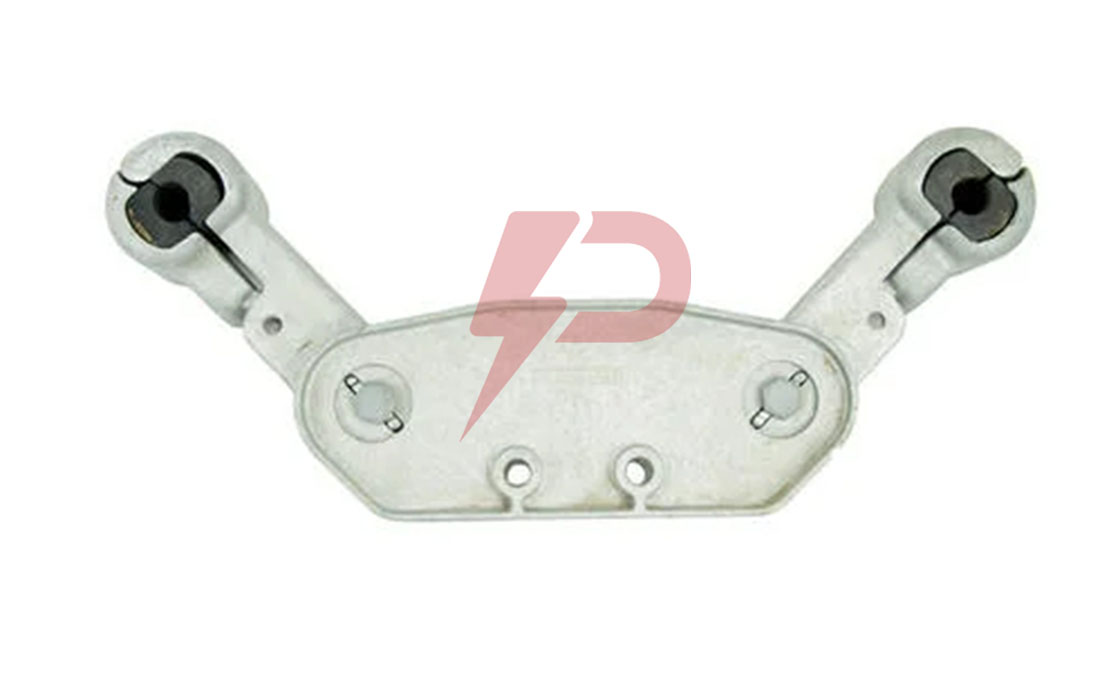
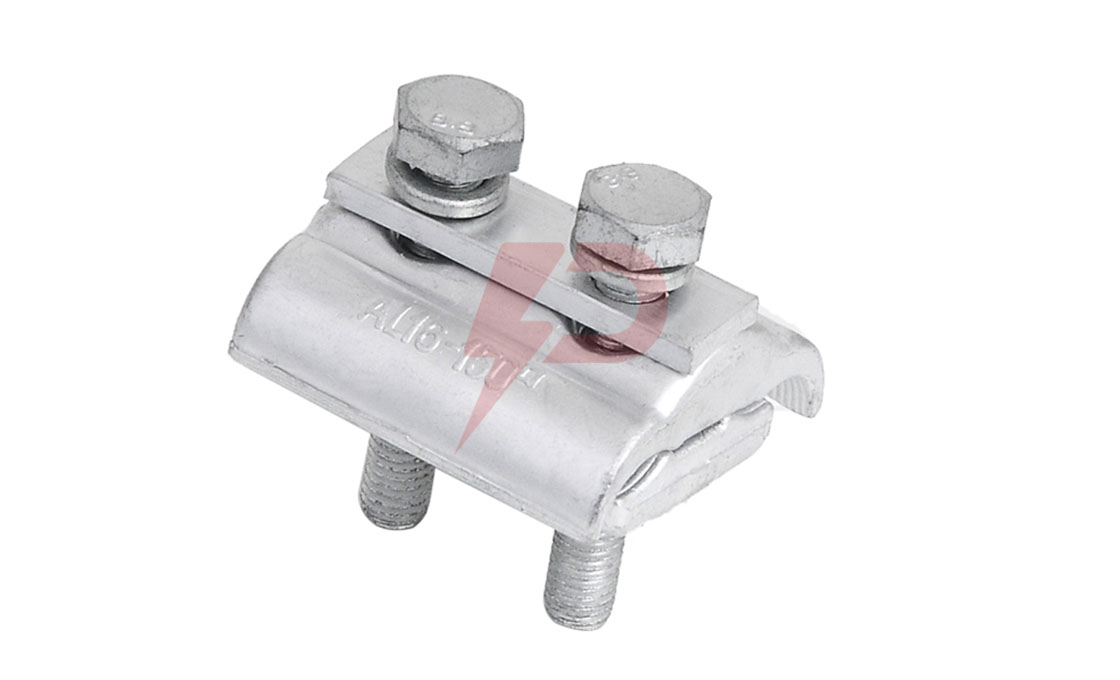
Triple Spacer Damper Drawing
| Type no | Suitable conductor | Dimension(mm) | Weight(kg) |
| L | |||
| FJZ3-35185 | LGJ-185/25,30,45 | 350 | 3.5 |
| FJZ3-35210 | LGJ-210/25,35,50 | 350 | 3.5 |
| FJZ3-35240 | LGJ-240/30,40,55 | 350 | 3.5 |
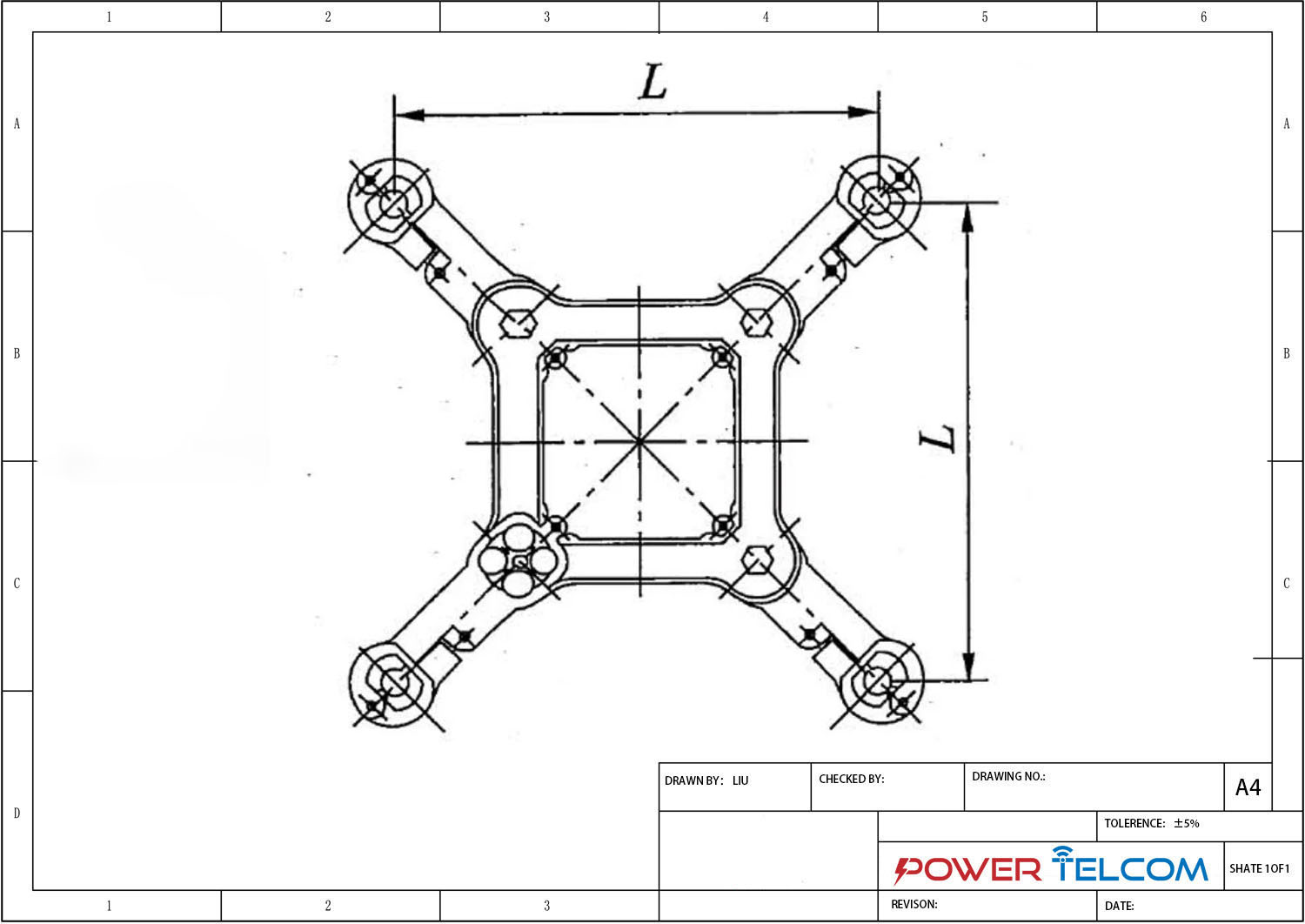
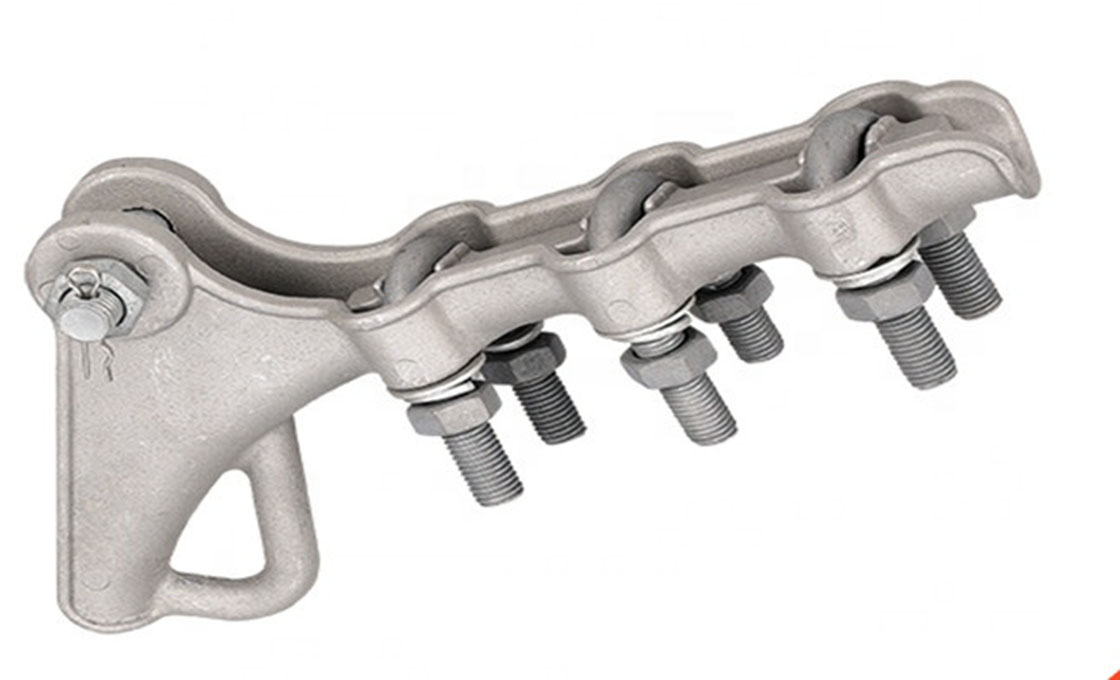
Square Frame Type Spacer Damper Drawing
| Cat.No. | Suitable Conductor | Dimensions(mm) L | Weight(kg) |
| JZF4-45300 | 23.0-24.5 | 450 | 7.5 |
| JZF4-45300J | 24.5-26.0 | 450 | 7.5 |
| JZF4-45400 | 26.0-28.0 | 450 | 7.5 |
| JZF4-45400J | 28.1-29.5 | 450 | 7.5 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do spacer dampers work?
Spacer dampers use elastomer parts to dissipate vibration energy on sub-conductors. The movable rubber components act as damping elements, absorbing aeolian vibration energy. This reduces wear on power fittings caused by conductor motion, increasing the longevity and safety of the transmission line.
What are the main components of a spacer damper?
A spacer damper typically consists of conductor clamps, a connecting frame, and damping elements. The clamps fasten the damper to the conductors, while the frame connects the clamps. The damping elements are made from elastic macro-molecular elastomers with high energy absorption capacity.
How do you choose the right spacer damper?
Select spacer dampers based on conductor dimensions, material quality, and transmission line requirements. Ensure there’s no external damage. Consider the specific needs of your overhead transmission line, as not all lines require spacer dampers. Consult manufacturer specifications for proper sizing and compatibility.
What are the installation requirements for spacer dampers?
Proper installation requires accurate span and catenary length calculations, correct spacer alignment, and appropriate tools. Ensure the damper size matches the conductor. Use proper torque when tightening bolts. Follow manufacturer guidelines for specific installation distances, typically keeping conductors 200-300 feet apart to avoid span clashing.
What are the key benefits of using spacer dampers?
Spacer dampers maintain conductor separation, control aeolian vibrations and subspan oscillations, reduce galloping, and protect against short circuit currents. They improve transmission line reliability, extend conductor lifespan, and minimize the risk of electrical faults and mechanical damage caused by wind-induced movements.
How do spacer dampers differ from vibration dampers?
Spacer dampers serve dual purposes of maintaining conductor spacing and damping vibrations in bundled conductors. Vibration dampers, like Stockbridge dampers, focus solely on dissipating vibration energy and can be used on both single and bundled conductors. Spacer dampers are specific to multi-conductor bundle systems.
What materials are used in spacer damper construction?
Spacer dampers typically use high-pressure die-cast aluminum alloy for the body and clamps, elastomers for the rubber elements, and various metals for hardware. Bolts, nuts, and washers are often galvanized steel, while safety plates and locking latches may be stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance.
How do spacer dampers handle different weather conditions?
Spacer dampers are designed to maintain their mechanical, elastic, and damping properties over a wide range of service temperatures. They help conductors withstand various weather conditions, including high winds, ice loading, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent performance throughout the transmission line’s lifetime.