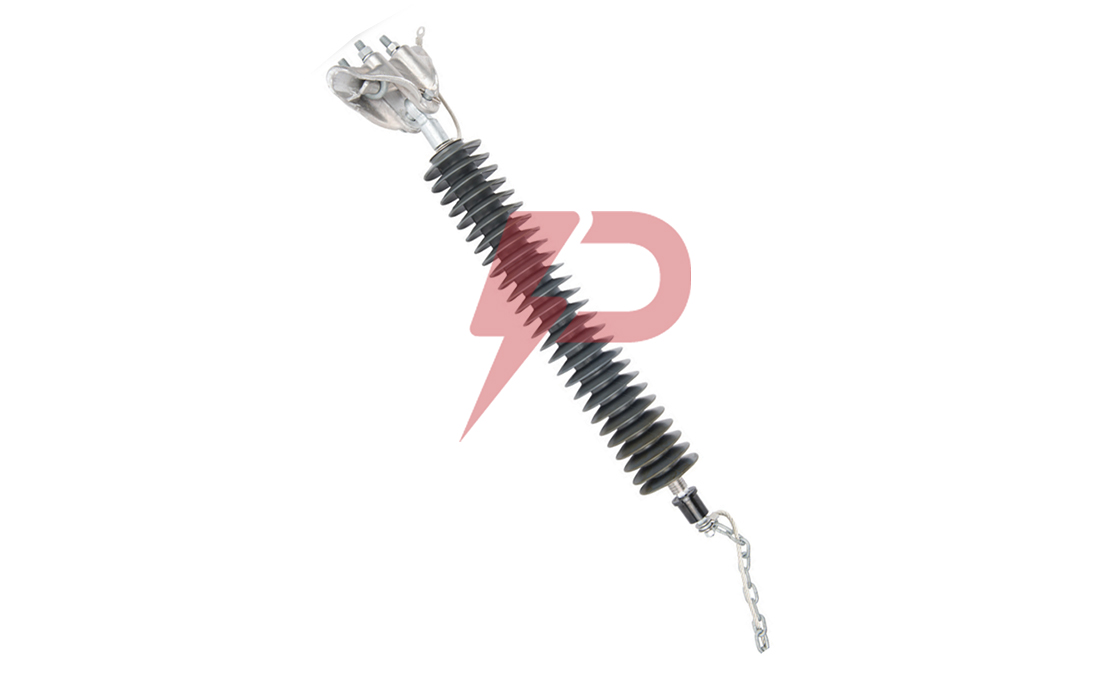
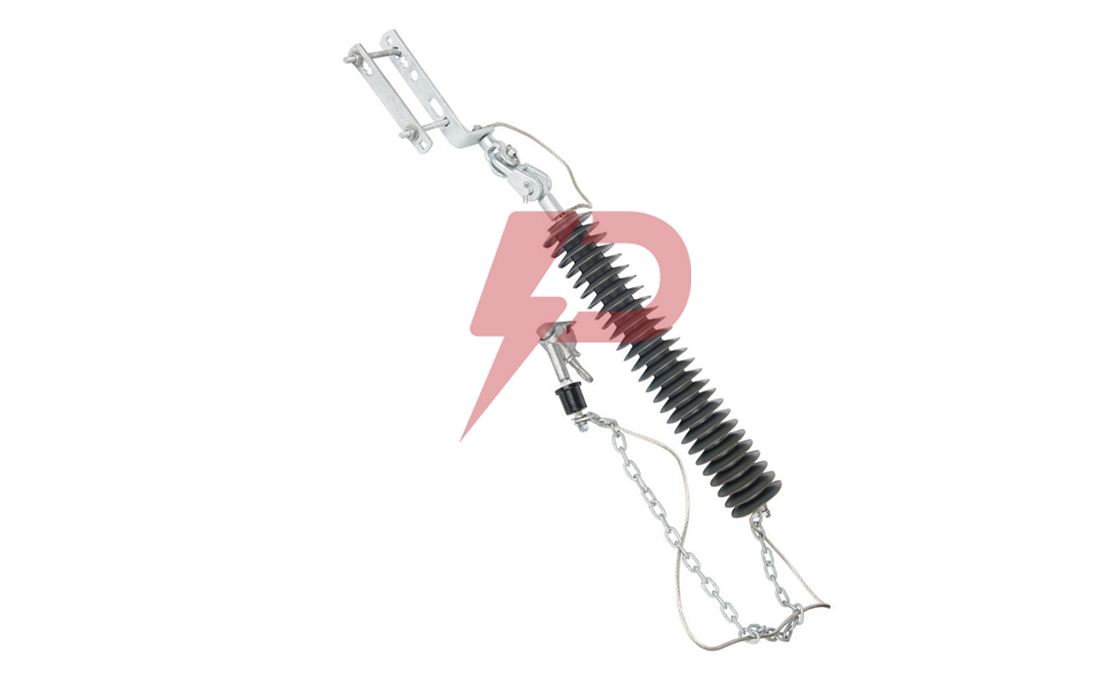
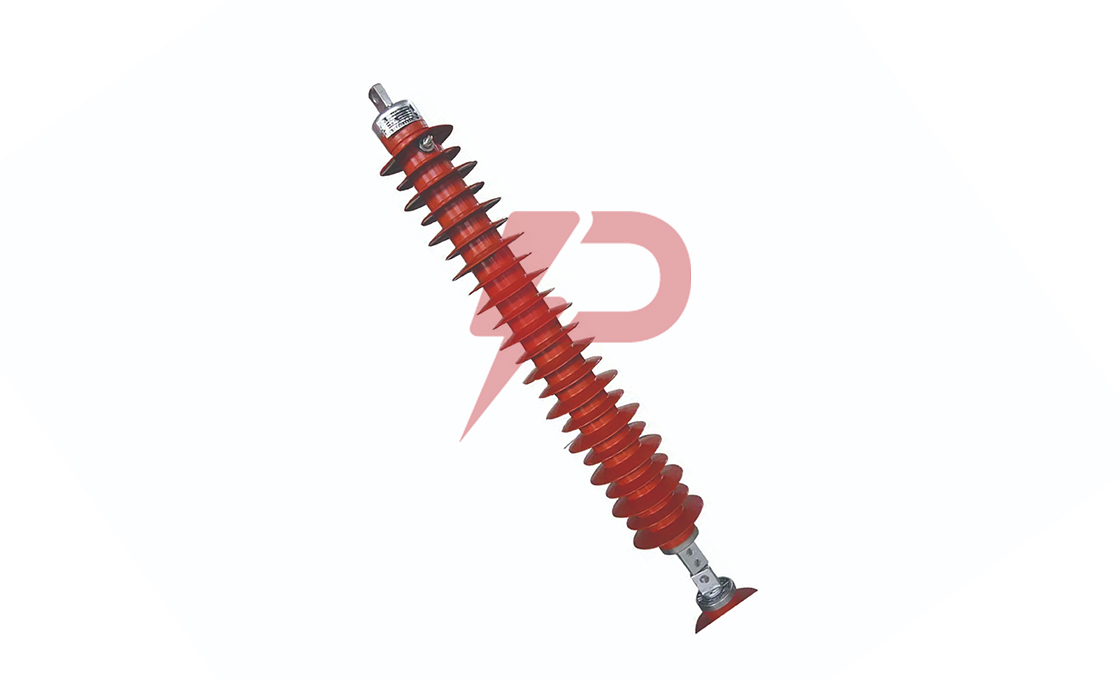
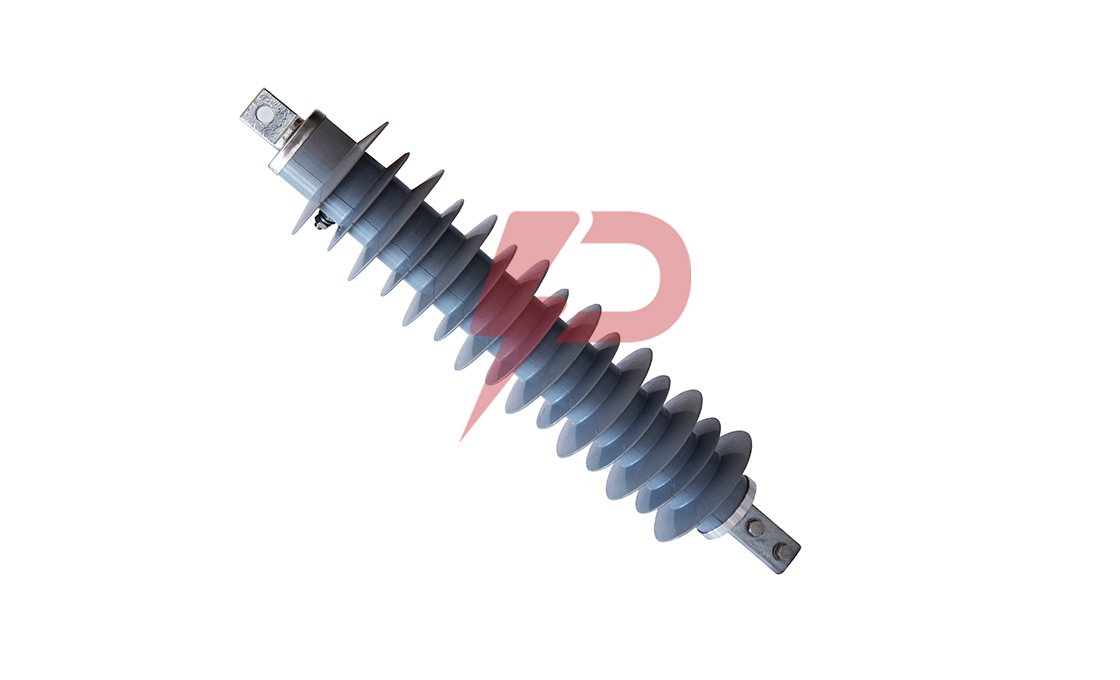
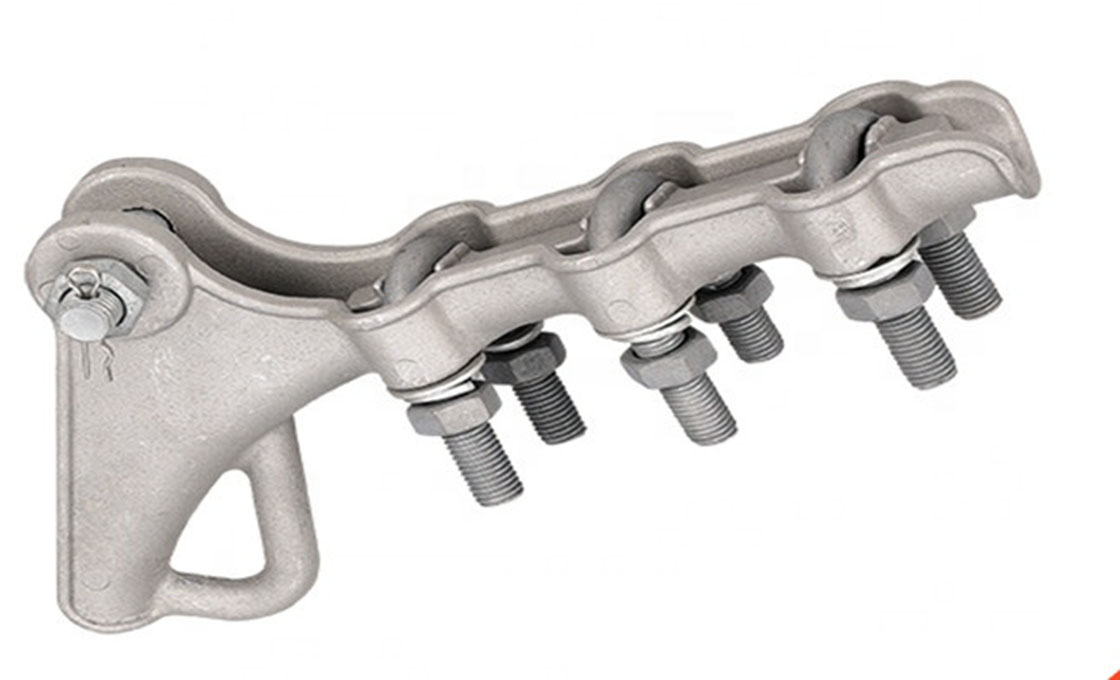
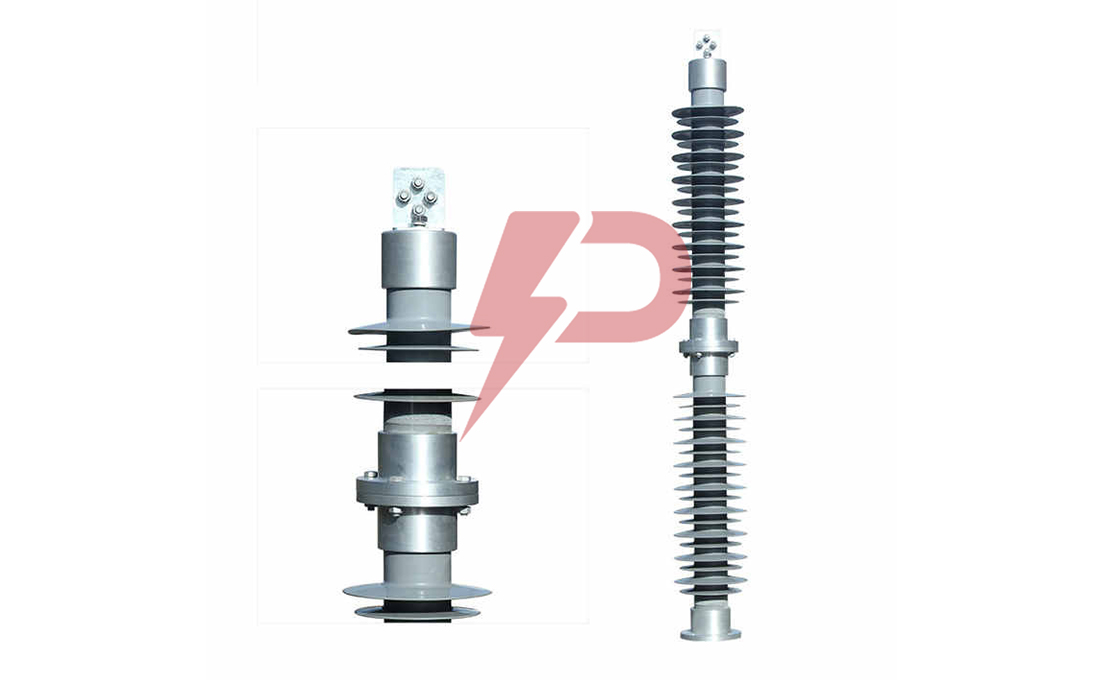
Non-Gapped Line Arrester
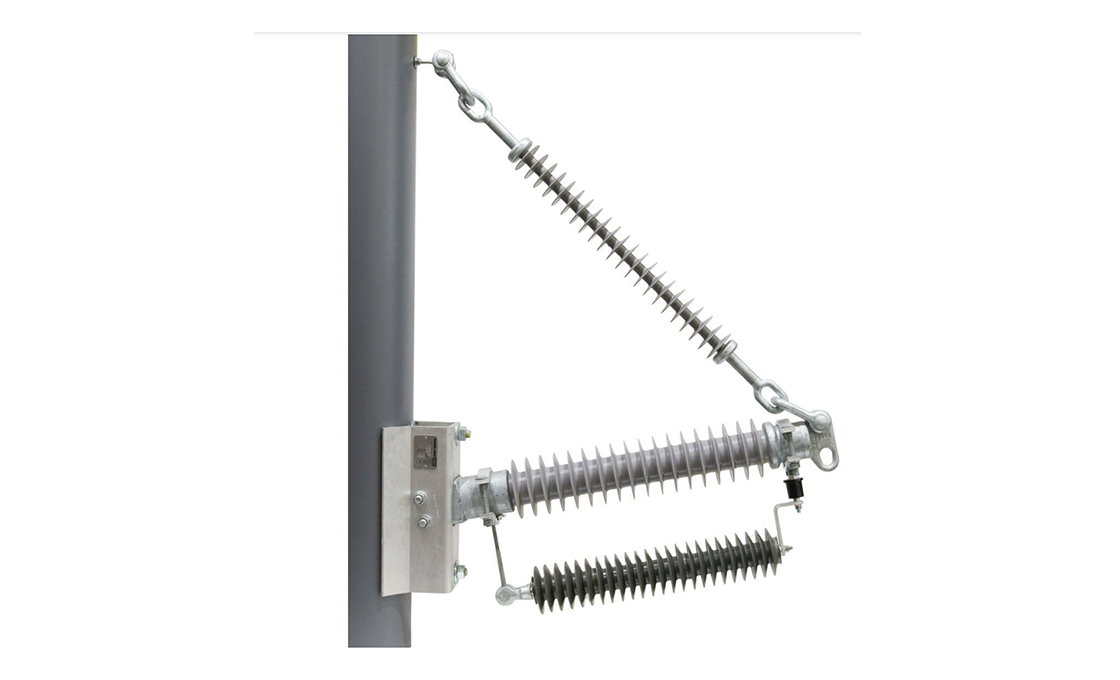
Non-Gapped Line Arresters (NGLA) are direct-connected surge protection devices without internal or external gap assemblies. These arresters utilize metal-oxide varistor blocks for lightning and switching surge protection in transmission lines. The NGLA can be configured for voltages from 15kV to 550kV and can be installed in three main variations: conductor-mounted, tower-mounted, or insulator-mounted configurations.
Non-Gapped Line Arresters incorporate disconnector mechanisms to facilitate fast reclosing and visually indicate overloaded units requiring replacement. The arresters share lightning charges between them as lightning strokes travel in two directions, making them highly effective for protecting line insulators. NGLAs are particularly valuable in systems without shield wires where there’s a higher probability of direct phase lightning strokes.
Key Features:
• Customizable mounting configurations for various line applications
• Lightweight polymer housing for enhanced durability
• Integrated ground lead disconnector for safety
• Direct connection without series gaps for improved response
• Coordinated protection with substation arresters
• Optimized rated voltage selection for different system requirements
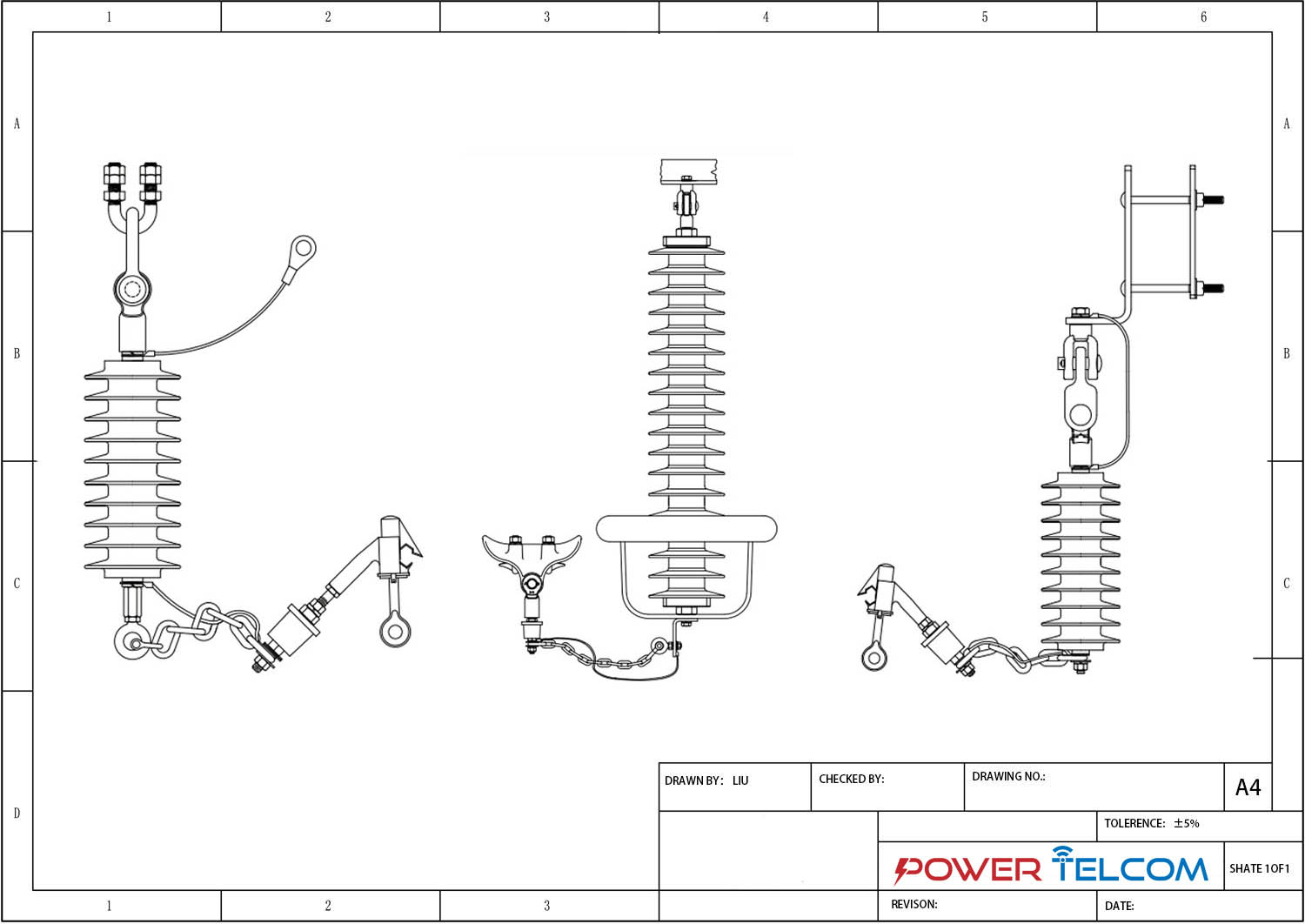
Non-Gapped Line Arrester Drawing
| Model type | Rated voltage | Continuous operating | DC U1mA reference voltage | Residual voltage(kV) | Discharge current | 0.75 U1mA leakage current (μA) | Creepage distance | ||||
| (kV) | voltage | (kV) | (mm/kV) | ||||||||
| (kV) | Lightning impulse current 8/20μs | Steep current impulse 1/10μs | Switching impulse current 30/60μs | 2ms | 4/10 μs high current (kA) | Degree III of pollution withstand | Degree IV of pollution withstand | ||||
| rectangular | |||||||||||
| current impulse withstand | |||||||||||
| (A) | |||||||||||
| YH5WX-51/134 | 51 | 40.8 | 73 | 134 | 154 | 114 | 400 | 65 | 50 | 32 | |
| YH5WX-51/122 | 51 | 40.8 | 73 | 122 | 140 | 104 | 400 | 65 | 50 | 32 | |
| YH5WX-96/232 | 96 | 72.5 | 134 | 232 | 267 | 198 | 400 | 65 | 50 | 28.2 | 31.2 |
| YH5WX-96/250 | 96 | 75 | 140 | 250 | 288 | 213 | 400 | 65 | 50 | 28.2 | 31.2 |
| YH10WX-96/232 | 96 | 72.5 | 134 | 232 | 267 | 198 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 28.2 | 31.2 |
| YH10WX-96/250 | 96 | 75 | 140 | 250 | 280 | 213 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 28.2 | 31.2 |
| YH10WX-100/260 | 100 | 78 | 145 | 260 | 291 | 221 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| YH10WX-102/266 | 102 | 79.6 | 148 | 266 | 297 | 226 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| YH10WX-108/281 | 108 | 84 | 157 | 281 | 315 | 239 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| YH10WX-200/520 | 200 | 156 | 290 | 520 | 582 | 442 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| 800 | |||||||||||
| YH10WX-204/532 | 204 | 159 | 296 | 532 | 594 | 452 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| 800 | |||||||||||
| YH10WX-216/562 | 216 | 168.5 | 314 | 562 | 630 | 478 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| 800 | |||||||||||
| YH10WX-312/760 | 312 | 237 | 442 | 760 | 847 | 643 | 600 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| 800 | |||||||||||
| YH10WX-444/1015 | 444 | 355 | 597 | 1015 | 1137 | 900 | 1200 | 100 | 50 | 26.8 | 31.4 |
| 1500 | |||||||||||
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

What is the primary purpose of Non-Gapped Line Arresters (NGLA)?
NGLAs are designed to prevent flashovers on overhead line insulator strings, not to protect the insulators themselves. Their main function is to reduce or eliminate lightning-induced outages that could impact network stability and have contractual consequences.
How do NGLAs differ from substation arresters?
While substation arresters protect valuable assets like power transformers from financial damage, NGLAs specifically focus on preventing flashovers on transmission line insulators. They are mounted on towers or near insulators to handle lightning and switching surge overvoltages.
Do NGLAs need to be installed on every tower?
Installation on every tower is usually not cost-effective except in cases where line tripping consequences are particularly harmful to the system. The number of NGLAs depends on tower footing resistance and outage reduction targets.
What are the mounting considerations for NGLAs?
NGLAs face higher physical stress than other arresters due to exposure to elements. They must withstand vibration, wind, torque, and impact stress. Mounting requirements are unique to each tower configuration and require careful consideration.
What determines the AC rating selection for NGLAs?
The Maximum Continuous Operating Voltage (MCOV) must be checked for temporary overvoltage withstand capability. The initial AC rating is generally a minimum value that may need to be increased to meet system constraints.
How does the presence of shield wires affect NGLA selection?
Systems without shield wires require NGLAs with higher charge capabilities due to increased risk of direct lightning strikes. Shield wire systems allow for lower charge requirements as lightning strokes are shared between arresters.