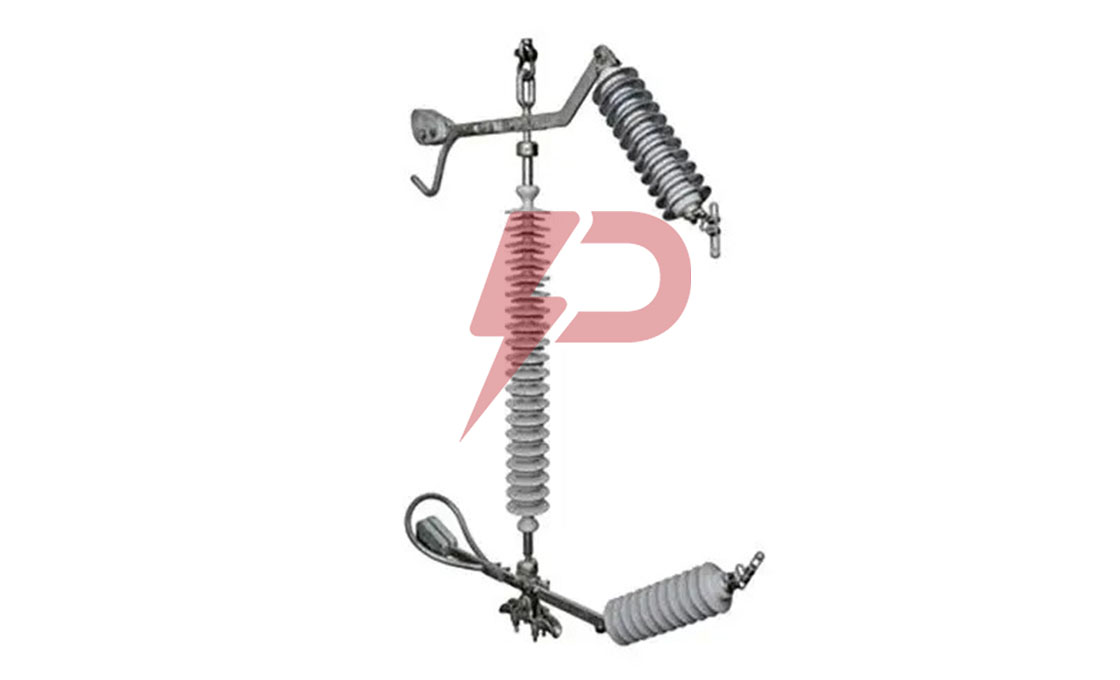
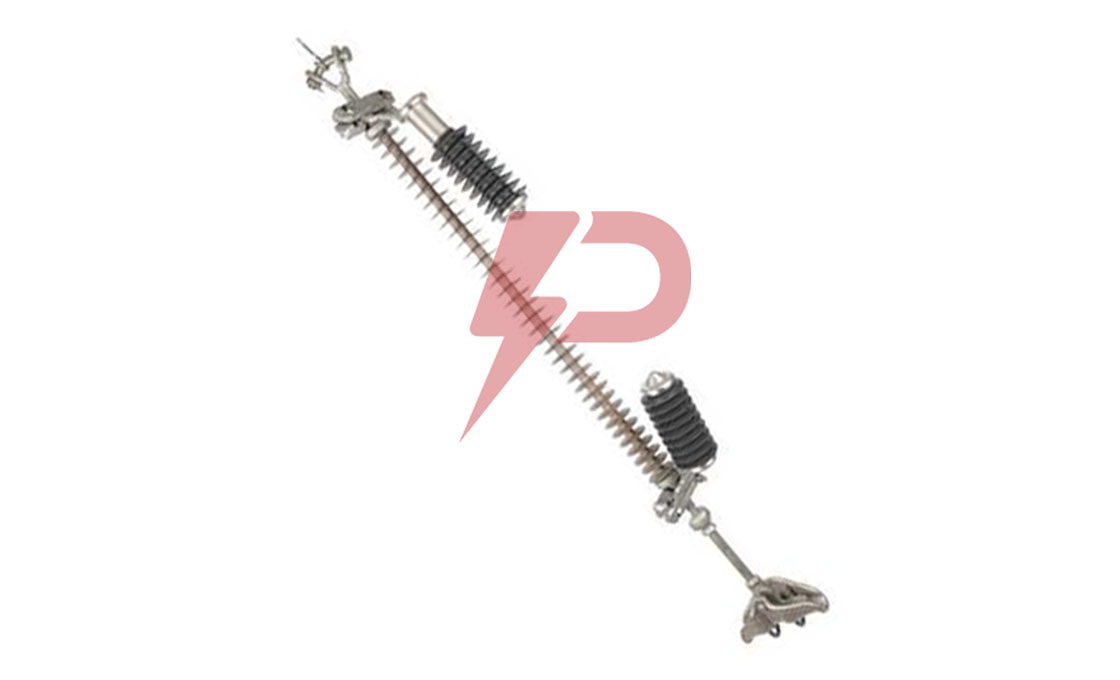
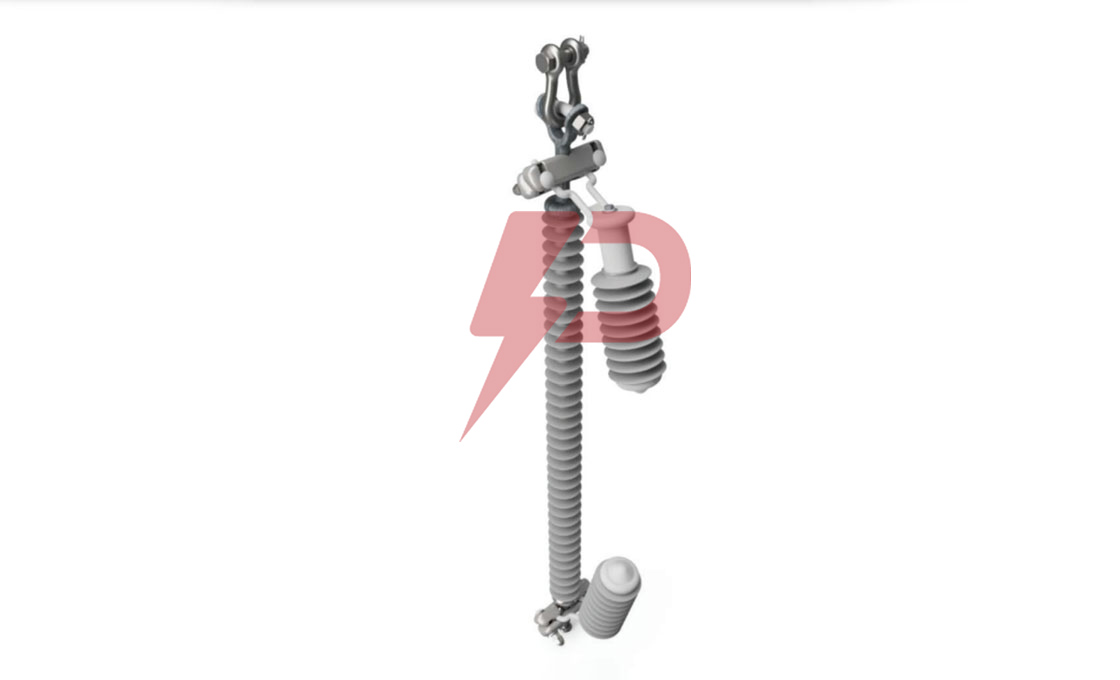
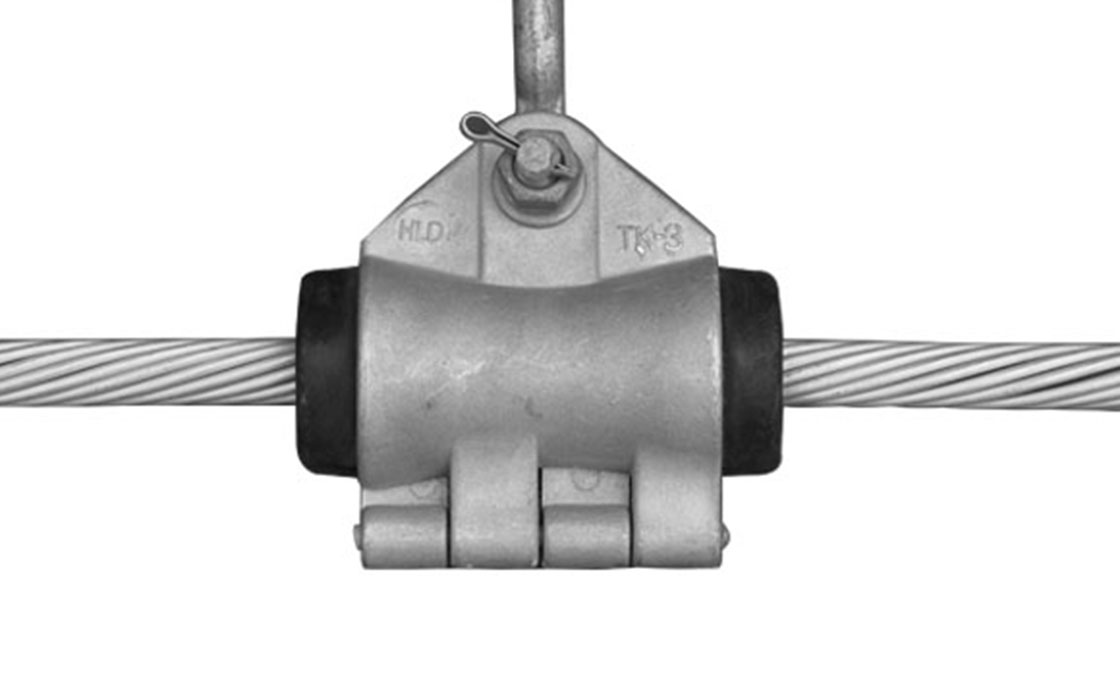
Parafoudre à espacement externe
Le parafoudre à espacement externe (EGLA) est un dispositif de protection contre les surtensions composé d'une unité de varistance en série (SVU) et un éclateur externe. Le dispositif protège les isolateurs de lignes de transmission contre les contournements induits par la foudre et les surtensions de commutation dans les systèmes électriques allant de 13,2 kV à 230 kV.. Lorsqu'une surtension se produit, l'écart se propage et canalise le courant à travers le SVU, qui limite et met ensuite fin au flux de courant avant qu'un courant de suivi de fréquence industrielle ne se développe.
L'EGLA est disponible en deux configurations: Type CEI pour la protection contre la foudre uniquement et type standard pour la protection contre la foudre et les surtensions de commutation. Le parafoudre à espacement externe se monte directement sur les lignes de transmission et nécessite un étalonnage précis de l'espacement des espaces en fonction de la tension du système et des conditions environnementales.. L'appareil peut être installé avec des configurations SVU simples ou doubles en fonction des exigences de tension.
Principales fonctionnalités:
– Aucune perte de fréquence industrielle en fonctionnement normal
– Capacité d'auto-réinitialisation sans intervention du disjoncteur
– Conception anti-panne garantie empêchant les pannes prolongées du système
– Besoins en matériaux de logement réduits grâce à 30% moins de ligne de fuite
– Vieillissement minimal des varistances à oxyde métallique grâce à l'isolation des espaces externes
– Options de montage flexibles pour les nouvelles installations ou les rénovations
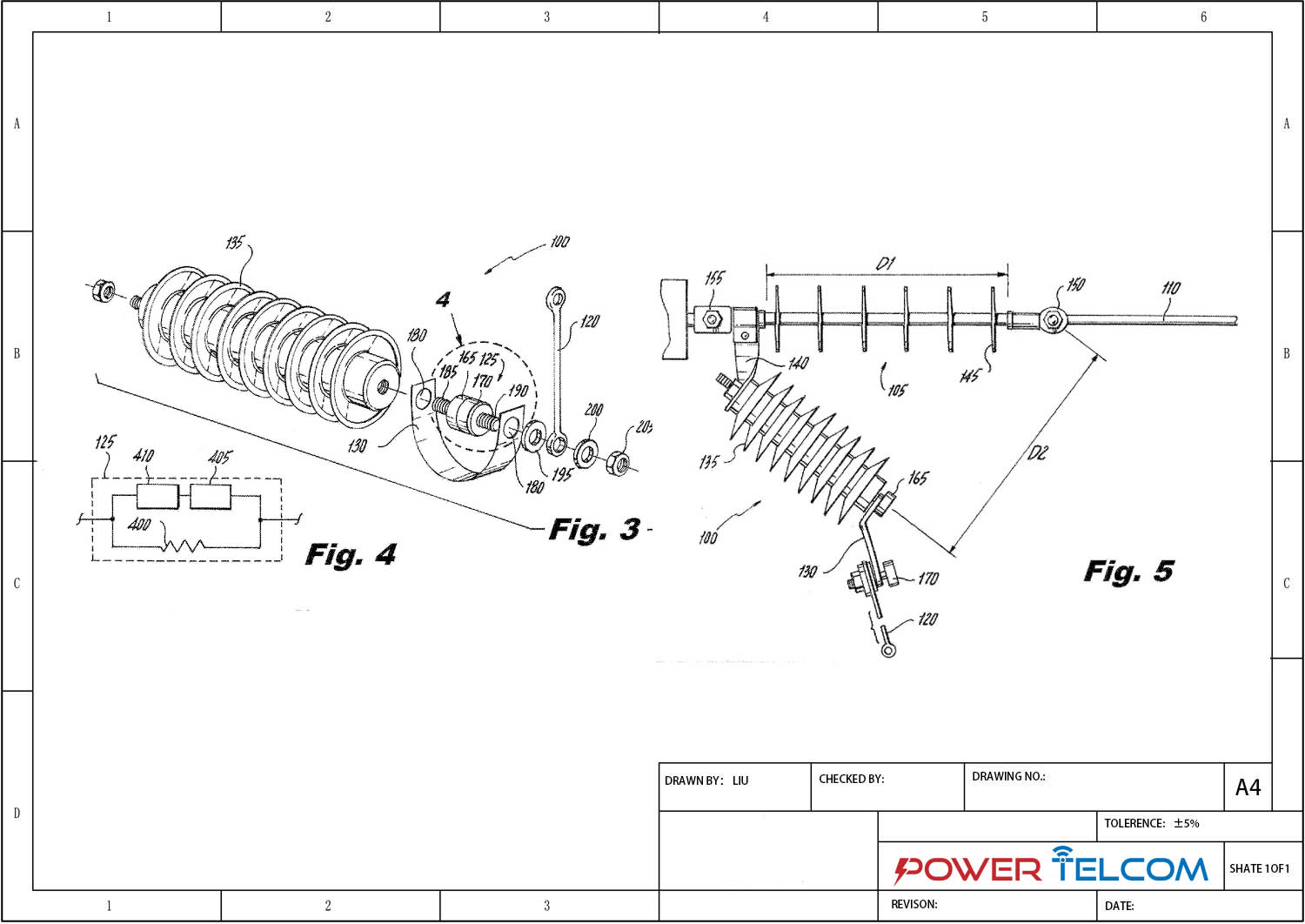
Dessin d'un parafoudre à espacement externe
Foire aux questions (FAQ)
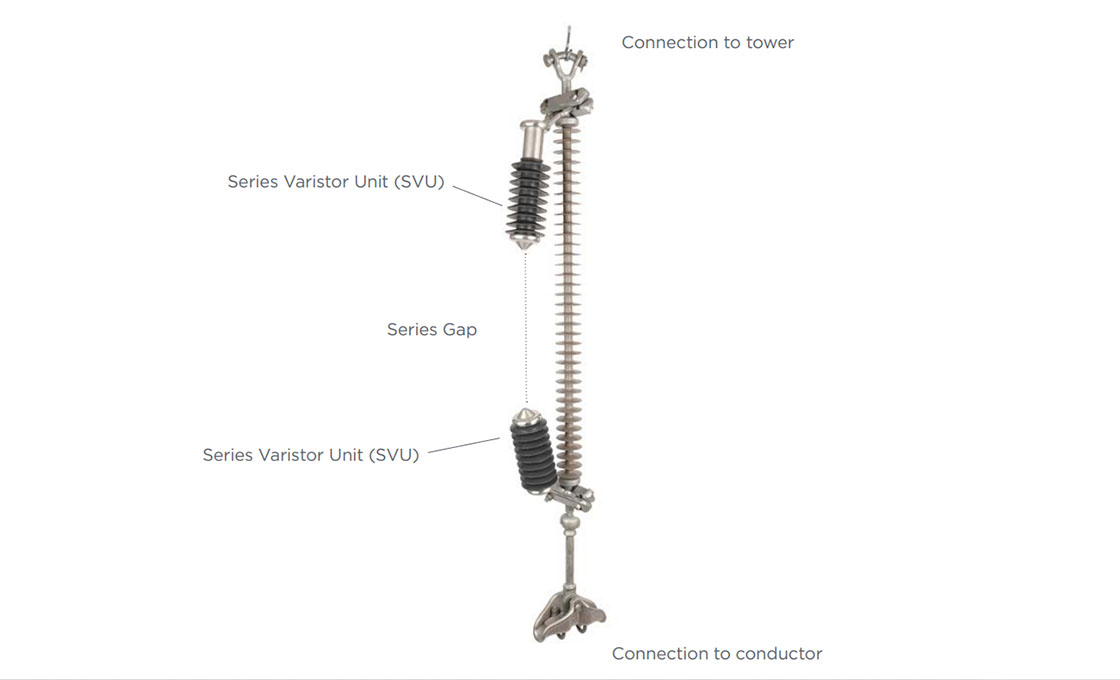
Comment fonctionne un EGLA?
L'EGLA combine un écart bien coordonné et une varistance qui fonctionnent ensemble. Quand la foudre frappe, l'espace se déclenche à une tension prédéterminée, puis les éléments MOV conduisent le courant de surtension vers la terre, limite suivre le courant, et éteindre l'arc électrique externe, le tout sans nécessiter le fonctionnement d'un disjoncteur.
Quels sont les éléments clés d’un EGLA?
Un EGLA se compose de deux composants principaux: une unité de varistance en série (SVU) qui fait office de partie parafoudre, et un éclateur externe en série. Les électrodes créent des points d'atterrissage d'arc durables, permettre l'ajustement de l'espacement des espaces, et fournissent des caractéristiques d'embrasement cohérentes.
Que se passe-t-il si l'espacement des espaces est incorrect?
Si l'espacement des espaces est inférieur au minimum, le risque de contournement lors d'une surtension temporaire augmente, potentiellement endommager le parafoudre. Si au-dessus du maximum, l'isolant peut s'embraser avant l'éclatement de l'espace, provoquant des pannes momentanées ou à long terme.
Quels sont les avantages d'EGLA par rapport à NGLA?
EGLA élimine le besoin de sectionneurs et d'anneaux corona, réduit la taille et le poids, et empêche les pannes temporaires de surtension. La conception est isolée de la tension du système, éliminant les problèmes de récupération thermique et les problèmes de fatigue du matériel.
Comment EGLA gère-t-il les conditions environnementales?
Bien que les performances des écarts puissent être affectées par les conditions environnementales, l'espace conserve sa capacité à s'embraser avant l'isolant protégé dans la plupart des conditions météorologiques. Cependant, EGLA ne peut pas protéger contre les contournements sévères induits par la pollution à la fréquence industrielle.
Quel est le rôle du lead management dans EGLA?
La gestion des sondes est plus simple avec EGLA qu'avec NGLA car les électrodes sont généralement plus courtes que les sondes.. Cela rend la gestion des électrodes moins difficile que la gestion des dérivations d'un NGLA.
Comment EGLA gère-t-il les situations de surcharge?
Lors de situations de surcharge, EGLA peut être équipé d'un sectionneur ou d'un indicateur de panne. Cette configuration permet à l'électrode de bouger après une surcharge, assurer un contournement critique complet (Directeur financier) récupération de l'isolant.
Quelle est la base de calcul de la distance minimale d'écartement?
Le réglage de l'écart minimum est calculé en fonction de la surtension de commutation maximale attendue. L'écart est suffisamment large pour éviter les étincelles lors des surtensions de commutation, en utilisant l'équation: G = 39.37[e(SS/1080) – 1.46], où G est la distance d'écart en pouces.