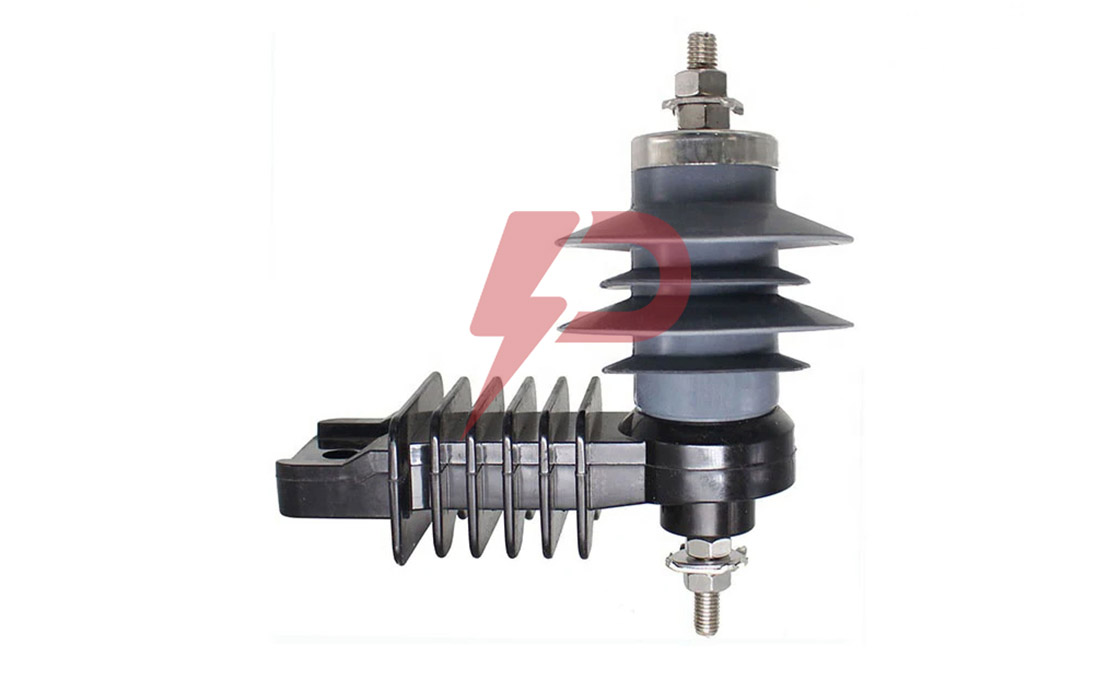
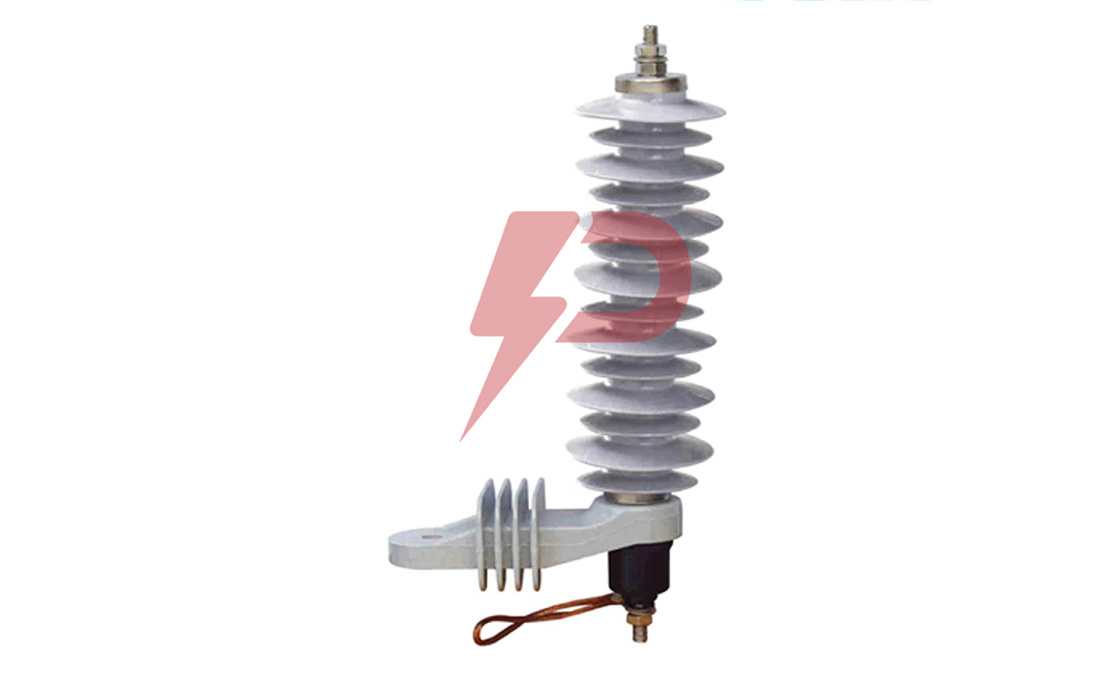
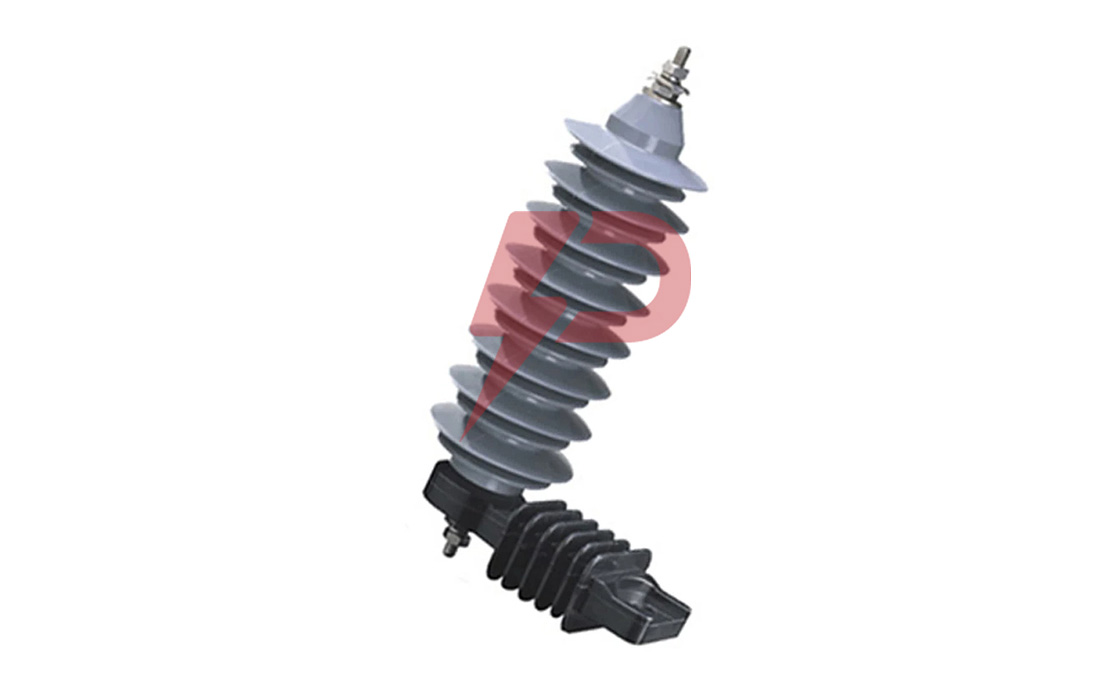
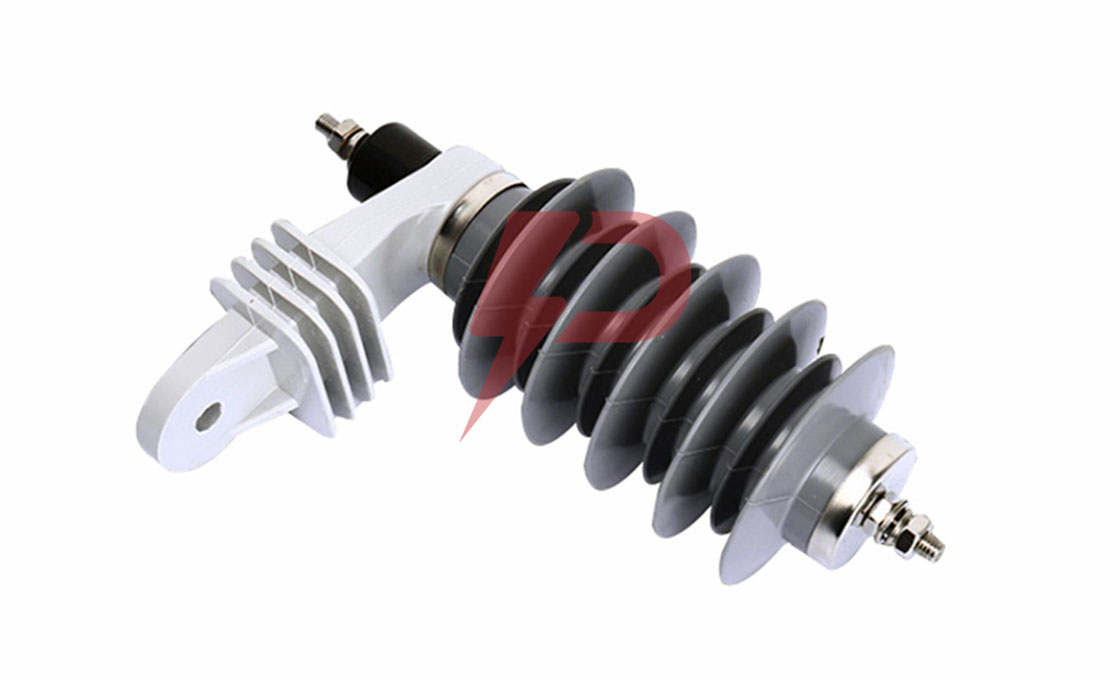
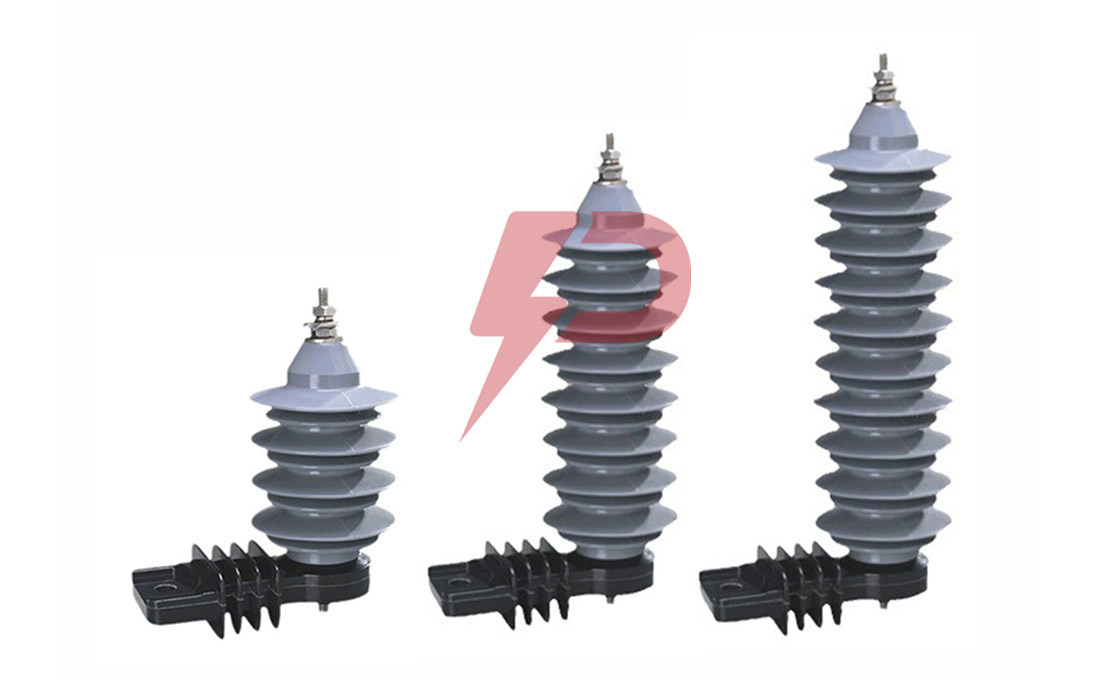
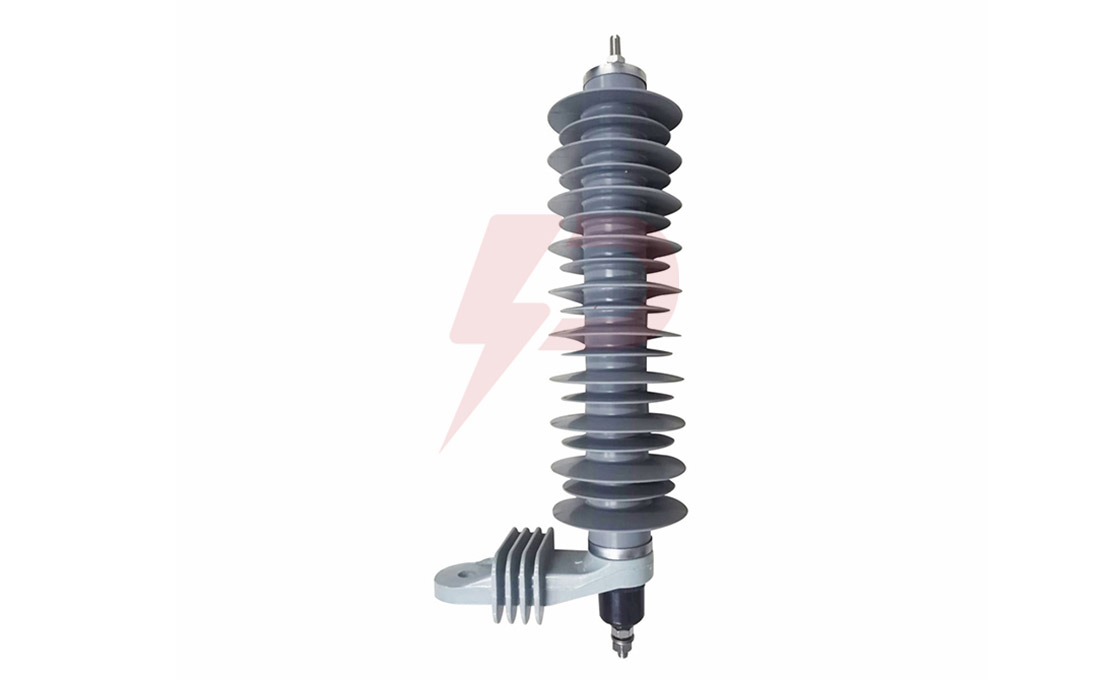
Distribution Arrester
Distribution Arresters are essential protective devices that safeguard electrical distribution systems against transient overvoltages and lightning strikes. These devices utilize metal oxide varistors (MOV) technology, featuring zinc oxide blocks as their primary component, which instantly become conductive during surge events to divert excess current to ground. Distribution Arresters work by clamping surge voltages to manageable levels, protecting vital equipment like transformers, switchgear, and distribution lines operating at voltages up to 72.5 kV.
Distribution Arresters come in three main classifications: Normal Duty (ND), Heavy Duty (HD), and Heavy Duty Riser. The Normal Duty type serves as baseline protection for areas with minimal lightning activity, while Heavy Duty variants offer enhanced protection for severe lightning-prone regions. The Heavy Duty Riser type, featuring larger diameter MOV discs, provides the highest level of protection and is typically installed to safeguard underground distribution cables and equipment. Modern Distribution Arresters utilize either porcelain or polymer housings, with silicone rubber being the predominant housing material due to its superior UV resistance and hydrophobic properties.
Features of Distribution Arresters:
• Advanced MOV technology for rapid surge response
• Multiple protection levels for various application needs
• Integrated disconnector functionality for visible failure indication
• Weather-resistant polymer housing options
• High mechanical strength and durability
• Comprehensive IEEE C62.11 compliance
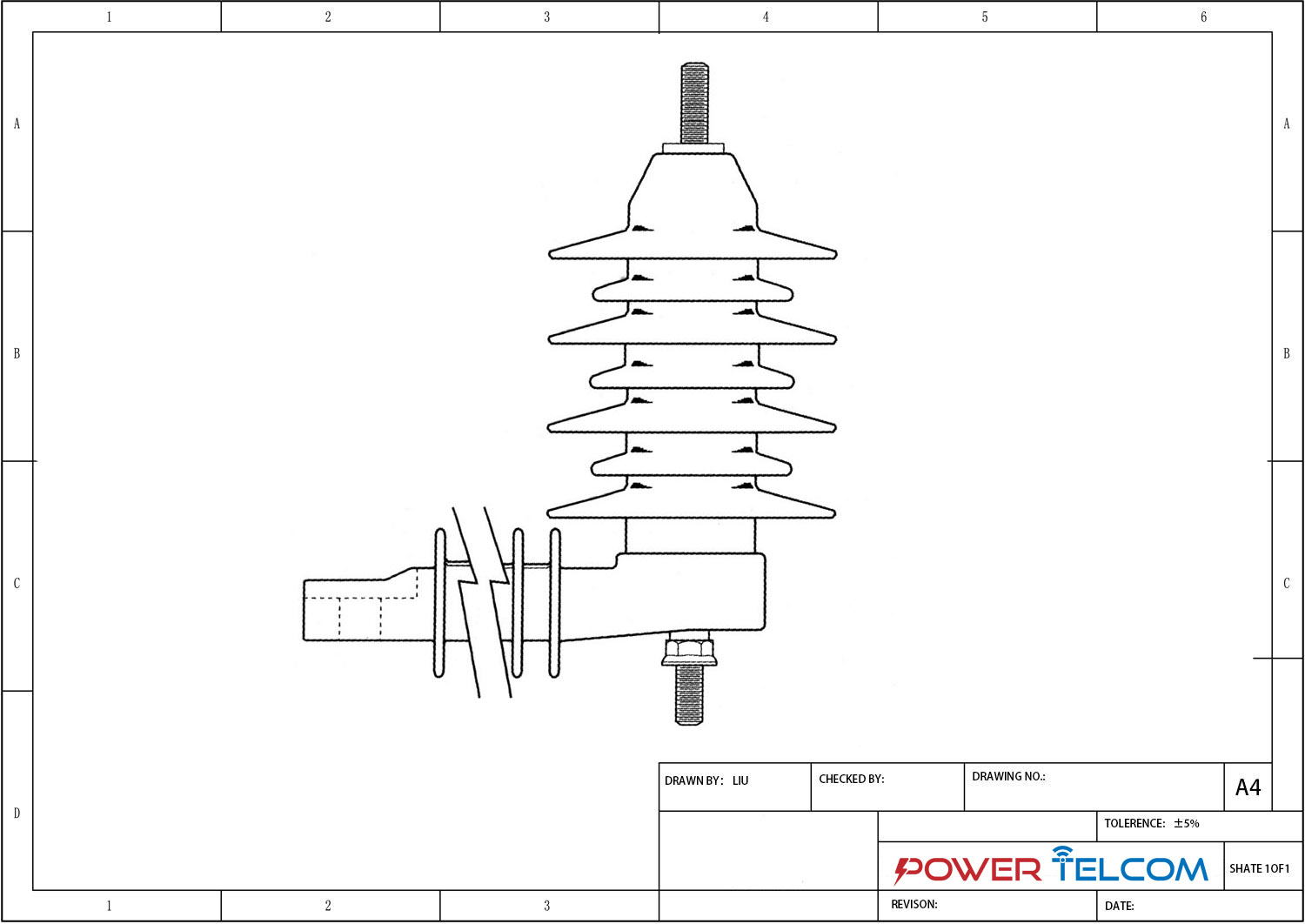
Distribution Arrester Drawing
| Type | Rated voltage (kV) | MCOV (kV) | Steep current impulse(kV) | 8/20us Lightning impulse(kV) | Repetitive charge transfer rating, Qrs (C) | 4/1 Ous High current impulse(kA) | 2ms rectangular current impulse withstand(A) | Arrester classification | |
| DA5W-3 | 3kV5kA | 3 | 2.4KV | 11 | 8.3 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-6 | 6kV5kA | 6 | 4.8KV | 20 | 16.6 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-9 | 9kV5kA | 9 | 7.2KV | 29.5 | 24.9 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-12 | 12kV 5kA | 12 | 9.6KV | 39 | 33.2 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-15 | 15kV 5kA | 15 | 12KV | 48.5 | 41.5 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-18 | 18kV 5kA | 18 | 14.4KV | 58 | 49.8 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-21 | 21kV 5kA | 21 | 16.8KV | 67.5 | 58.1 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-24 | 24kV 5kA | 24 | 19.2KV | 77 | 66.4 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-27 | 27kV 5kA | 27 | 21.6KV | 86.5 | 74.7 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-30 | 30kV 5kA | 30 | 24KV | 96 | 83 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-33 | 33kV 5kA | 33 | 26.4KV | 105.5 | 91.3 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA5W-36 | 36kV 5kA | 36 | 28.8KV | 115 | 99.6 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DM |
| DA10W-3 | 3kV lOkA | 3 | 2.4KV | 11 | 8.3 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-6 | 6kV lOkA | 6 | 4.8KV | 20 | 16.6 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-9 | 9kV lOkA | 9 | 7.2KV | 29.5 | 24.9 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-12 | 12kV lOkA | 12 | 9.6KV | 39 | 33.2 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-15 | 15kV lOkA | 15 | 12KV | 48.5 | 41.5 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-18 | 18kV lOkA | 18 | 14.4KV | 58 | 49.8 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-21 | 21kV lOkA | 21 | 16.8KV | 67.5 | 58.1 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-24 | 24kV lOkA | 24 | 19.2KV | 77 | 66.4 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-27 | 27kV lOkA | 27 | 21.6KV | 86.5 | 74.7 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-30 | 3OkV lOkA | 30 | 24KV | 96 | 83 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-33 | 33kV lOkA | 33 | 26.4KV | 105.5 | 91.3 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
| DA10W-36 | 36kV lOkA | 36 | 28.8KV | 115 | 99.6 | 0.4 | 100 | 400 | DH |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How do distribution arresters enhance grid reliability?
Distribution arresters improve grid reliability by diverting excess energy to ground, preventing outages, minimizing disruptions to customers, and maintaining stable voltage profiles. They can also be integrated into smart grid systems for real-time monitoring of system performance and health.
What is the purpose of a distribution surge arrester?
A distribution surge arrester protects electrical infrastructure against sudden voltage increases or “surges” caused by lightning strikes or other transient events. It limits the voltage of the power distribution system and diverts excess current to ground, preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
How do ZnO MOV blocks work in distribution arresters?
Zinc oxide MOV (Metal Oxide Varistor) blocks in distribution arresters provide a low-resistance path for current. They conduct high levels of electricity, absorbing voltage and dissipating excess energy while limiting damage to the distribution system.
What factors should be considered when rating a distribution surge arrester?
When rating distribution surge arresters, consider the surge rating (expressed as a voltage rating), which indicates its operating conditions and energy diversion capacity. Also, take into account the size, construction materials, and dimensions of the arrester, as these affect overall performance.
Where should distribution surge arresters be used?
Distribution surge arresters should be used in distribution networks to protect lines, transformers, and other electrical equipment from lightning strikes or power faults. This helps reduce downtime, repair costs, and revenue loss due to outages.
What are the benefits of polymeric housings in distribution arresters?
Polymeric housings, particularly those made of silicone rubber, offer superior pollution performance, improved safety, and better sealing against moisture ingress compared to traditional porcelain housings. They also perform better under high contamination conditions due to long-term hydrophobic properties.
What is the role of a disconnector in distribution arresters?
Most distribution arresters are equipped with a disconnector device that separates the ground lead if the arrester fails. This ensures that arrester failure does not cause a permanent outage and provides a visible indication for maintenance staff to replace the arrester.